Immune Sensing of Cell Death through Recognition of Histone Sequences by C-Type Lectin-Receptor-2d Causes Inflammation and Tissue Injury
- PMID: 31859049
- PMCID: PMC6962543
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.11.013
Immune Sensing of Cell Death through Recognition of Histone Sequences by C-Type Lectin-Receptor-2d Causes Inflammation and Tissue Injury
Abstract
The immune system monitors the health of cells and is stimulated by necrosis. Here we examined the receptors and ligands driving this response. In a targeted screen of C-type lectin receptors, a Clec2d reporter responded to lysates from necrotic cells. Biochemical purification identified histones, both free and bound to nucleosomes or neutrophil extracellular traps, as Clec2d ligands. Clec2d recognized poly-basic sequences in histone tails and this recognition was sensitive to post-translational modifications of these sequences. As compared with WT mice, Clec2d-/- mice exhibited reduced proinflammatory responses to injected histones, and less tissue damage and improved survival in a hepatotoxic injury model. In macrophages, Clec2d localized to the plasma membrane and endosomes. Histone binding to Clec2d did not stimulate kinase activation or cytokine production. Rather, histone-bound DNA stimulated endosomal Tlr9-dependent responses in a Clec2d-dependent manner. Thus, Clec2d binds to histones released upon necrotic cell death, with functional consequences to inflammation and tissue damage.
Keywords: C-type lectin; Clec2d; DAMPs; Toll-like receptor; histone acetylation; histones; inflammation; liver injury; macrophages; pattern recognition receptor.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
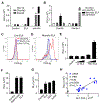
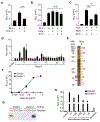
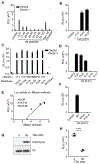
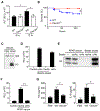
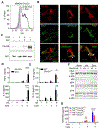
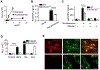
Comment in
-
Clec2d Joins the Cell Death Sensor Ranks.Immunity. 2020 Jan 14;52(1):6-8. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.12.015. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 31951550
References
-
- Ahrens S, Zelenay S, Sancho D, Hanc P, Kjaer S, Feest C, Fletcher G, Durkin C, Postigo A, Skehel M, et al. (2012). F-actin is an evolutionarily conserved damage-associated molecular pattern recognized by DNGR-1, a receptor for dead cells. Immunity 36, 635–645. - PubMed
-
- Alcover A, Alarcon B, and Di Bartolo V (2018). Cell Biology of T Cell Receptor Expression and Regulation. Annu Rev Immunol 36, 103–125. - PubMed
-
- Allam R, Kumar SV, Darisipudi MN, and Anders HJ (2014). Extracellular histones in tissue injury and inflammation. J Mol Med (Berl) 92, 465–472. - PubMed
-
- Augusto LA, Decottignies P, Synguelakis M, Nicaise M, Le Marechal P, and Chaby R (2003). Histones: a novel class of lipopolysaccharide-binding molecules. Biochemistry 42, 3929–3938. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

