CD247 expression is associated with differentiation and classification in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 31861005
- PMCID: PMC6940041
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018407
CD247 expression is associated with differentiation and classification in ovarian cancer
Abstract
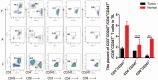
Ovarian cancer (OC) is one of the most common malignant tumors in female reproductive system and most OC cases are diagnosed at an advanced stage with the overall 5-year survival rate below 40%. The function of CD247 enhances T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) signaling cascade and it is necessary for assembling of the TCR/CD3 complex on the surface of T lymphocytes. It is well established that defective CD247 function leads to impaired activation of T cells upon engagement of the TCR.Flow cytometry was used to examine the difference of CD247 T lymphocyte between the OC and ovarian cyst, immunohistochemistry analysis was used to investigate the correlation between CD247 expression and clinicopathologic features of epithelial OC patients.Our study showed that the expression of CD247 in peripheral blood lymphocytes from patients with OC is decreased compared with ovarian cyst patients and the expression of CD247 in tumor infiltrating lymphocytes with cancer tissue is decreased compared with adjacent tissues. We showed that abnormal expression of CD247 was related with differentiation and classification in OC.Our findings suggested that CD247-targeted treatment could be used as a potential therapeutic strategy for OC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Narod S. Can advanced-stage ovarian cancer be cured? Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2016;13:255–61. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Coleman MP, Quaresma M, Berrino F, et al. Cancer survival in five continents: a worldwide population-based study (CONCORD). Lancet Oncol 2008;9:730–56. - PubMed
-
- Hede K. Environmental protection: studies highlight importance of tumor microenvironment. J Natl Cancer Inst 2004;96:1120–1. - PubMed
-
- Germain RN, Stefanova I. The dynamics of T cell receptor signaling: complex orchestration and the key roles of tempo and cooperation. Annu Rev Immunol 1999;17:467–522. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

