The association between rs12807809 polymorphism in neurogranin gene and risk of schizophrenia: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 31861040
- PMCID: PMC6940187
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018518
The association between rs12807809 polymorphism in neurogranin gene and risk of schizophrenia: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The correlation between single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs12807809 in Neurogranin (NRGN) gene and Schizophrenia (SCZ) was investigated by several studies, whereas the results were conflicting. Thus, we performed the present meta-analysis to combine and analyze the available studies in order to provide a more accurate result on the association of rs12807809 polymorphism in NRGN gene and SCZ vulnerability.
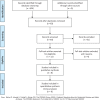
Methods: A comprehensive retrieval in PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, Cochrane Library and Wanfang was performed for relevant studies on the relationship of rs12807809 polymorphism and SCZ. Summary odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence interval (95% CI) were calculated in allelic, homozygous, heterozygous, dominant and recessive model to appraise the association.
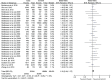
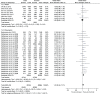
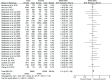
Results: The meta-analysis included 8 studies containing 12552 SCZ cases and 34783 controls. The results showed a statistically significant correlation between SCZ and rs12807809 polymorphism in overall population in allelic model (OR = 1.10, 95%CI 1.04-1.17). However, subgroup analysis indicated the association only existed in Caucasians but not Asian.
Conclusion: The results of present meta-analysis suggested significant association between SNP rs12807809 in NRGN gene and SCZ susceptibility in Caucasians but not Asians.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Minor allele C of rs12807809 polymorphism in NRGN contributes to the severity of psychosis in patients with Schizophrenia in South Indian population.Neurosci Lett. 2017 May 10;649:107-111. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.04.008. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Neurosci Lett. 2017. PMID: 28389239
-
Functional genetic variation at the NRGN gene and schizophrenia: evidence from a gene-based case-control study and gene expression analysis.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2012 Jun;159B(4):405-13. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32043. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2012. PMID: 22461181
-
Analysis of neurogranin (NRGN) in schizophrenia.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2011 Jul;156B(5):532-5. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.31191. Epub 2011 May 2. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2011. PMID: 21538840
-
Association between rs738409 polymorphism in patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 (PNPLA3) gene and hepatocellular carcinoma susceptibility: Evidence from case-control studies.Gene. 2019 Feb 15;685:143-148. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.11.012. Epub 2018 Nov 4. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30403964 Review.
-
Gene polymorphisms of DISC1 is associated with schizophrenia: Evidence from a meta-analysis.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2018 Feb 2;81:64-73. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.10.008. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29031911 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurogranin: A Potential Biomarker of Neurological and Mental Diseases.Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Oct 6;12:584743. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.584743. eCollection 2020. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33132903 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rethelyi JM, Benkovits J, Bitter I. Genes and environments in schizophrenia: The different pieces of a manifold puzzle. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2013;37:2424–37. - PubMed
-
- Gejman PV, Sanders AR, Kendler KS. Genetics of schizophrenia: new findings and challenges. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 2011;12:121–44. - PubMed
-
- Girard SL, Dion PA, Rouleau GA. Schizophrenia genetics: putting all the pieces together. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2012;12:261–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

