S1P/S1P Receptor Signaling in Neuromuscolar Disorders
- PMID: 31861214
- PMCID: PMC6941007
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20246364
S1P/S1P Receptor Signaling in Neuromuscolar Disorders
Abstract
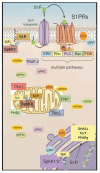
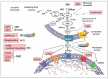
The bioactive sphingolipid metabolite, sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P), and the signaling pathways triggered by its binding to specific G protein-coupled receptors play a critical regulatory role in many pathophysiological processes, including skeletal muscle and nervous system degeneration. The signaling transduced by S1P binding appears to be much more complex than previously thought, with important implications for clinical applications and for personalized medicine. In particular, the understanding of S1P/S1P receptor signaling functions in specific compartmentalized locations of the cell is worthy of being better investigated, because in various circumstances it might be crucial for the development or/and the progression of neuromuscular diseases, such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, myasthenia gravis, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Keywords: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease; ceramide; duchenne muscular dystrophy; myasthenia gravis; nervous system; neuromuscular disease; skeletal muscle; sphingolipids; sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Loh K.C., Leong W.I., Carlson M.E., Oskouian B., Kumar A., Fyrst H., Zhang M., Proia R.L., Hoffman E.P., Saba J.D. Sphingosine-1-phosphate enhances satellite cell activation in dystrophic muscles through a S1PR2/STAT3 signaling pathway. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e37218. doi: 10.1371/annotation/7e7ac57d-30ae-4e49-9138-e3bdbe3491d2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ieronimakis N., Pantoja M., Hays A.L., Dosey T.L., Qi J., Fischer K.A., Hoofnagle A.N., Sadilek M., Chamberlain J.S., Ruohola-Baker H., et al. Increased sphingosine-1-phosphate improves muscle regeneration in acutely injured mdx mice. Skelet. Muscle. 2013;3:20. doi: 10.1186/2044-5040-3-20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

