The Terrestrial Carnivorous Plant Utricularia reniformis Sheds Light on Environmental and Life-Form Genome Plasticity
- PMID: 31861318
- PMCID: PMC6982007
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21010003
The Terrestrial Carnivorous Plant Utricularia reniformis Sheds Light on Environmental and Life-Form Genome Plasticity
Abstract
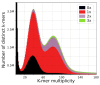
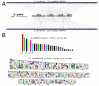
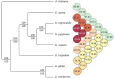
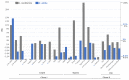
Utricularia belongs to Lentibulariaceae, a widespread family of carnivorous plants that possess ultra-small and highly dynamic nuclear genomes. It has been shown that the Lentibulariaceae genomes have been shaped by transposable elements expansion and loss, and multiple rounds of whole-genome duplications (WGD), making the family a platform for evolutionary and comparative genomics studies. To explore the evolution of Utricularia, we estimated the chromosome number and genome size, as well as sequenced the terrestrial bladderwort Utricularia reniformis (2n = 40, 1C = 317.1-Mpb). Here, we report a high quality 304 Mb draft genome, with a scaffold NG50 of 466-Kb, a BUSCO completeness of 87.8%, and 42,582 predicted genes. Compared to the smaller and aquatic U. gibba genome (101 Mb) that has a 32% repetitive sequence, the U. reniformis genome is highly repetitive (56%). The structural differences between the two genomes are the result of distinct fractionation and rearrangements after WGD, and massive proliferation of LTR-retrotransposons. Moreover, GO enrichment analyses suggest an ongoing gene birth-death-innovation process occurring among the tandem duplicated genes, shaping the evolution of carnivory-associated functions. We also identified unique patterns of developmentally related genes that support the terrestrial life-form and body plan of U. reniformis. Collectively, our results provided additional insights into the evolution of the plastic and specialized Lentibulariaceae genomes.
Keywords: ABC transporters; evolution; genome fractionation; transcription factors; transposable elements; whole-genome duplication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


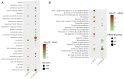
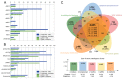
References
-
- Taylor P. The Genus Utricularia-A Taxonomic Monograph. The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew; London, UK: 1989.
-
- Lan T., Renner T., Ibarra-Laclette E., Farr K.M., Chang T.H., Cervantes-Pérez S.A., Zheng C., Sankoff D., Tang H., Purbojati R.W., et al. Long-read sequencing uncovers the adaptive topography of a carnivorous plant genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2017;114:E4435–E4441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1702072114. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 13/25164-6/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 13/05144-0/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 18/02285-6/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 11/22215-3/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 460990/2014-4/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development - CNPq
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

