Inhibitory Effects of Myrtucommuacetalone 1 (MCA-1) from Myrtus communis on Inflammatory Response in Mouse Macrophages
- PMID: 31861488
- PMCID: PMC6983223
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25010013
Inhibitory Effects of Myrtucommuacetalone 1 (MCA-1) from Myrtus communis on Inflammatory Response in Mouse Macrophages
Abstract
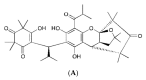
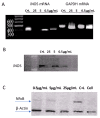
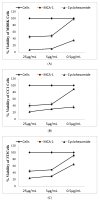
(1) Introduction: Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO) are key signaling molecules that play important roles in the progression of inflammatory disorders. The objective of this study was to explore the use of myrtucommuacetalone-1 (MCA-1), as a novel compound of natural origin and a potential anti-inflammatory agent. (2) Methodology: The anti-inflammatory potential of MCA-1, which was isolated from Myrthus communis Linn, was determined by assaying superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and nitric oxide production in macrophages. Furthermore, the effects of the compound were analyzed via phosphorylation and translocation of the transcription factor NF kappa B, which is a key regulator of iNOS activation. The effect of MCA-1 on the inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) enzyme was also examined using in silico docking studies. The anticancer potential for MCA-1 was evaluated with an MTT cytotoxic assay. (3) Results: In stimulated macrophages, MCA-1 inhibited superoxide production by 48%, hydrogen peroxide by 53%, and nitric oxide (NO) with an IC50 of <1 µg/mL. MCA-1 also showed a very strong binding pattern within the active site of the inducible nitric oxide synthase enzyme. Furthermore, 25 µg/mL of MCA-1 inhibited inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and abolished transcription factor (NFκB) phosphorylation and translocation to the nucleus. Cytotoxicity analyses of MCA-1 on 3T3 mouse fibroblasts, CC1 liver cell line, J774.2, macrophages and MDBK bovine kidney epithelial cell, yielded IC50 values of 6.53 ± 1.2, 4.6 ± 0.7, 5 ± 0.8, and 4.6 ± 0.7, µg/mL, respectively. (4) Conclusion: Our results suggest that MCA-1, a major phloroglucinol-type compound, shows strong anti-inflammatory activity and has a potential to be a leading therapeutic agent in the future.
Keywords: inflammation; macrophages; nitric oxide; respiratory burst.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Anti-Inflammatory Activity and ROS Regulation Effect of Sinapaldehyde in LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages.Molecules. 2020 Sep 7;25(18):4089. doi: 10.3390/molecules25184089. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32906766 Free PMC article.
-
Puerarin suppresses production of nitric oxide and inducible nitric oxide synthase in lipopolysaccharide-induced N9 microglial cells through regulating MAPK phosphorylation, O-GlcNAcylation and NF-κB translocation.Int J Oncol. 2012 May;40(5):1610-8. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1331. Epub 2012 Jan 13. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22246431
-
Xanthii fructus inhibits inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages through suppressing NF-κB and JNK/p38 MAPK.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 24;176:394-401. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.11.020. Epub 2015 Nov 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26560439
-
Nepetoidin B, a Natural Product, Inhibits LPS-stimulated Nitric Oxide Production via Modulation of iNOS Mediated by NF-κB/MKP-5 Pathways.Phytother Res. 2017 Jul;31(7):1072-1077. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5828. Epub 2017 May 15. Phytother Res. 2017. PMID: 28504466
-
Anti-Infective Peptides to Enhance the Host Innate Response: Design, Development and Delivery.Protein Pept Lett. 2018;25(12):1101-1107. doi: 10.2174/0929866525666181101104945. Protein Pept Lett. 2018. PMID: 30381058 Review.
Cited by
-
The therapeutic value of Myrtus communis L.: an updated review.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Jul;397(7):4579-4600. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-02958-3. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38319389 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

