Protopine Protects Mice against LPS-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Inhibiting Apoptosis and Inflammation via the TLR4 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 31861525
- PMCID: PMC6982873
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25010015
Protopine Protects Mice against LPS-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Inhibiting Apoptosis and Inflammation via the TLR4 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
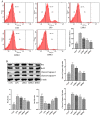
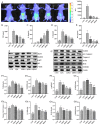
Corydalis humosa Migo is a traditional Chinese medicine that clears away damp heat, relieves sore. Protopine (PRO) is an alkaloid component isolated from C. humosa Migo. However, the role of protopine in acute kidney injury (AKI) has not yet been reported. This study aims to investigate the effect and mechanism of protopine isolated from C. humosa Migo on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced AKI in mice. Inflammation accumulation was assessed by small animal living imaging. The blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and serum creatinine (Scr) were measured to assess the effects of protopine on renal function in LPS-induced AKI. The levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin-2 (IL-2), interferon-γ (IFN-γ), and (interleukin-10) IL-10 in serum were detected by cytometric bead array. Flow cytometry was used to detect the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in primary kidney cells. The proportions of granulocytes, neutrophils, and macrophages in peripheral blood were examined to evaluate the effect of protopine on immune cells in mice with AKI. Toll-like receptor (TLR4) and apoptotic signaling pathway were detected by Western blot analysis. The results showed that protopine markedly improved the renal function, relieve inflammation, reversed inflammatory cytokines, transformed apoptosis markers, and regulated the TLR4 signaling pathway in mice with AKI induced by LPS. The protopine isolated from C. humosa Migo protected mice against LPS-induced AKI by inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation via the TLR4 signaling pathway, thus providing a molecular basis for a novel medical treatment of AKI.
Keywords: TLR4 signaling pathway; acute kidney injury; apoptosis; inflammation; protopine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Quoilin C., Mouithys-Mickalad A., Lecart S., Fontaine-Aupart M.-P., Hoebeke M. Evidence of oxidative stress and mitochondrial respiratory chain dysfunction in an in vitro model of sepsis-induced kidney injury. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Bioenerg. 2014;1837:1790–1800. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2014.07.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Robert S.W., Wang W. Acute renal failure and sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;351:159–169. - PubMed
-
- Choudhary G.S., Al-Harbi S., Almasan A. Caspase-3 activation is a critical determinant of genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015;1219:1–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

