Sphingolipids in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Ceramide Turnover
- PMID: 31861664
- PMCID: PMC6982102
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21010040
Sphingolipids in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Ceramide Turnover
Abstract
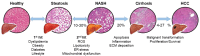
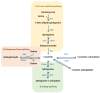
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has emerged as one of the main causes of chronic liver disease worldwide. NAFLD comprises a group of conditions characterized by the accumulation of hepatic lipids that can eventually lead to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the fifth most common cancer type with a poor survival rate. In this context, several works have pointed out perturbations in lipid metabolism and, particularly, changes in bioactive sphingolipids, as a hallmark of NAFLD and derived HCC. In the present work, we have reviewed existing literature about sphingolipids and the development of NAFLD and NAFLD-derived HCC. During metabolic syndrome, considered a risk factor for steatosis development, an increase in ceramide and sphigosine-1-phosphate (S1P) have been reported. Likewise, other reports have highlighted that increased sphingomyelin and ceramide content is observed during steatosis and NASH. Ceramide also plays a role in liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, acting synergistically with S1P. Finally, during HCC, metabolic fluxes are redirected to reduce cellular ceramide levels whilst increasing S1P to support tumor growth.
Keywords: HCC; Metabolic syndrome; NAFLD; NASH; S1P; ceramide; cirrhosis; lipidomics; metabolomics; sphingolipids; sphingomyelin.
Conflict of interest statement
María Luz Martínez-Chantar advises for Mitotherapeutix LLC. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Manifold Roles of Ceramide Metabolism in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1372:157-168. doi: 10.1007/978-981-19-0394-6_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35503180
-
Sphingolipids at the Crossroads of NAFLD and Senescence.Adv Cancer Res. 2018;140:155-190. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2018.05.002. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Adv Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30060808 Review.
-
Insights into the roles and pathomechanisms of ceramide and sphigosine-1-phosphate in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Jan 1;19(1):311-330. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.78525. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36594091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipidomic biomarkers and mechanisms of lipotoxicity in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Nov 20;144:293-309. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.05.029. Epub 2019 May 29. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 31152791 Review.
-
Ceramide de novo synthesis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Aug;202:115157. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115157. Epub 2022 Jun 28. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35777449 Review.
Cited by
-
Navigating through the Lipid Metabolism Maze: Diagnosis and Prognosis Metabolites of Hepatocellular Carcinoma versus Compensated Cirrhosis.J Clin Med. 2022 Feb 26;11(5):1292. doi: 10.3390/jcm11051292. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35268381 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicant-Induced Metabolic Alterations in Lipid and Amino Acid Pathways Are Predictive of Acute Liver Toxicity in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 4;21(21):8250. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218250. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33158035 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the lipid profiles of hairtail (Trichiurus lepturus) muscle during air-drying via liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis.Food Chem X. 2023 Feb 24;17:100610. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2023.100610. eCollection 2023 Mar 30. Food Chem X. 2023. PMID: 36974190 Free PMC article.
-
Liver Lipidomics Analysis Revealed the Novel Ameliorative Mechanisms of L-Carnitine on High-Fat Diet-Induced NAFLD Mice.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 10;15(6):1359. doi: 10.3390/nu15061359. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36986087 Free PMC article.
-
Applying Lipidomics to Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Clinical Perspective.Nutrients. 2023 Apr 20;15(8):1992. doi: 10.3390/nu15081992. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37111211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

