Serine-Arginine Protein Kinase 1 (SRPK1) as a Prognostic Factor and Potential Therapeutic Target in Cancer: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 31861708
- PMCID: PMC7017105
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9010019
Serine-Arginine Protein Kinase 1 (SRPK1) as a Prognostic Factor and Potential Therapeutic Target in Cancer: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives
Abstract
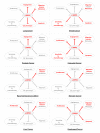
Cancer, a heterogeneous disease composed of tumor cells and microenvironment, is driven by deregulated processes such as increased proliferation, invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, and evasion of apoptosis. Alternative splicing, a mechanism led by splicing factors, is implicated in carcinogenesis by affecting any of the processes above. Accumulating evidence suggests that serine-arginine protein kinase 1 (SRPK1), an enzyme that phosphorylates splicing factors rich in serine/arginine domains, has a prognostic and potential predictive role in various cancers. Its upregulation is correlated with higher tumor staging, grading, and shorter survival. SRPK1 is also highly expressed in the premalignant changes of some cancers, showing a potential role in the early steps of carcinogenesis. Of interest, its downregulation in preclinical models has mostly been tumor-suppressive and affected diverse processes heterogeneously, depending on the oncogenic context. In addition, targeting SRPK1 has enhanced sensitivity to platinum-based chemotherapy in some cancers. Lastly, its aberrant function has been noted not only in cancer cells but also in the endothelial cells of the microenvironment. Although the aforementioned evidence seems promising, more studies are needed to reinforce the use of SRPK1 inhibitors in clinical trials.
Keywords: TNM staging; alternative splicing; angiogenesis; apoptosis; cancer survival; chemotherapy resistance; metastasis; personalized medicine; prognosis; serine-arginine protein kinase 1 (SRPK1).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serine-arginine protein kinase 1 is associated with breast cancer progression and poor patient survival.Med Oncol. 2014 Aug;31(8):83. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0083-8. Epub 2014 Jun 25. Med Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24961466
-
Expression of SRPK1 in gliomas and its role in glioma cell lines viability.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jul;37(7):8699-707. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4738-7. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26738865
-
Serine-arginine protein kinase 1 (SRPK1) is elevated in gastric cancer and plays oncogenic functions.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 28;8(37):61944-61957. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18734. eCollection 2017 Sep 22. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28977917 Free PMC article.
-
SRPK1 inhibition in vivo: modulation of VEGF splicing and potential treatment for multiple diseases.Biochem Soc Trans. 2012 Aug;40(4):831-5. doi: 10.1042/BST20120051. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012. PMID: 22817743 Review.
-
Serine arginine protein kinase 1 (SRPK1): a moonlighting protein with theranostic ability in cancer prevention.Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Feb;46(1):1487-1497. doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-4545-5. Epub 2018 Dec 8. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30535769 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein-Protein Interaction Inhibitor of SRPKs Alters the Splicing Isoforms of VEGF and Inhibits Angiogenesis.iScience. 2021 Apr 20;24(5):102423. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102423. eCollection 2021 May 21. iScience. 2021. PMID: 33997701 Free PMC article.
-
SRSF5 Regulates the Expression of BQ323636.1 to Modulate Tamoxifen Resistance in ER-Positive Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 13;15(8):2271. doi: 10.3390/cancers15082271. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37190199 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-659-3p inhibits osteosarcoma progression and metastasis by inhibiting cell proliferation and invasion via targeting SRPK1.BMC Cancer. 2022 Aug 29;22(1):934. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10029-0. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36038837 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of SRPK1, a key splicing regulator, exhibits antitumor and chemotherapeutic-sensitizing effects on extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma cells.BMC Cancer. 2022 Oct 27;22(1):1100. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10158-6. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36303126 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the dark cancer phosphoproteome using machine-learned co-regulation of phosphosites.Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 20;16(1):2766. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57993-2. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40113755 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

