Brain-Derived Extracellular Vesicle microRNA Signatures Associated with In Utero and Postnatal Oxycodone Exposure
- PMID: 31861723
- PMCID: PMC7016745
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9010021
Brain-Derived Extracellular Vesicle microRNA Signatures Associated with In Utero and Postnatal Oxycodone Exposure
Abstract
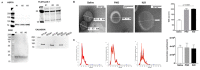
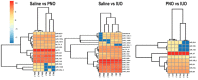
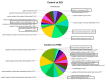
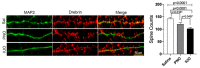
Oxycodone (oxy) is a semi-synthetic opioid commonly used as a pain medication that is also a widely abused prescription drug. While very limited studies have examined the effect of in utero oxy (IUO) exposure on neurodevelopment, a significant gap in knowledge is the effect of IUO compared with postnatal oxy (PNO) exposure on synaptogenesis-a key process in the formation of synapses during brain development-in the exposed offspring. One relatively unexplored form of cell-cell communication associated with brain development in response to IUO and PNO exposure are extracellular vesicles (EVs). EVs are membrane-bound vesicles that serve as carriers of cargo, such as microRNAs (miRNAs). Using RNA-Seq analysis, we identified distinct brain-derived extracellular vesicle (BDEs) miRNA signatures associated with IUO and PNO exposure, including their gene targets, regulating key functional pathways associated with brain development to be more impacted in the IUO offspring. Further treatment of primary 14-day in vitro (DIV) neurons with IUO BDEs caused a significant reduction in spine density compared to treatment with BDEs from PNO and saline groups. In summary, our studies identified for the first time, key BDE miRNA signatures in IUO- and PNO-exposed offspring, which could impact their brain development as well as synaptic function.
Keywords: RNA-Seq; brain derived EVs; in utero; oxycodone; postnatal.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors approve the contents presented in the current manuscript and declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Distinct Synaptic Vesicle Proteomic Signatures Associated with Pre- and Post-Natal Oxycodone-Exposure.Cells. 2022 May 25;11(11):1740. doi: 10.3390/cells11111740. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35681434 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Adolescent Nicotine Exposure in Pre- and Post-natal Oxycodone Exposed Offspring.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2023 Sep;18(3):413-426. doi: 10.1007/s11481-023-10074-x. Epub 2023 Jun 23. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37351737
-
Characterization of the intergenerational impact of in utero and postnatal oxycodone exposure.Transl Psychiatry. 2020 Sep 23;10(1):329. doi: 10.1038/s41398-020-01012-z. Transl Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32968044 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in extracellular vesicles: potential cancer biomarkers.J Hum Genet. 2017 Jan;62(1):67-74. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2016.87. Epub 2016 Jul 7. J Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 27383658 Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles: New Endogenous Shuttles for miRNAs in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy?Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 4;21(18):6486. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186486. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32899898 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In utero and post-natal opioid exposure followed by mild traumatic brain injury contributes to cortical neuroinflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and behavioral deficits in juvenile rats.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2023 Jul 28;32:100669. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2023.100669. eCollection 2023 Oct. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2023. PMID: 37588011 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in animal models of prenatal opioid exposure.Trends Neurosci. 2024 May;47(5):367-382. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2024.03.005. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Trends Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38614891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct Synaptic Vesicle Proteomic Signatures Associated with Pre- and Post-Natal Oxycodone-Exposure.Cells. 2022 May 25;11(11):1740. doi: 10.3390/cells11111740. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35681434 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling Psychiatric Disorders through Neural Single-Cell Transcriptomics Approaches.Genes (Basel). 2023 Mar 22;14(3):771. doi: 10.3390/genes14030771. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36981041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The future of Extracellular Vesicles as Theranostics - an ISEV meeting report.J Extracell Vesicles. 2020 Sep 4;9(1):1809766. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2020.1809766. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020. PMID: 33144926 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zosel A., Bartelson B.B., Bailey E., Lowenstein S., Dart R. Characterization of adolescent prescription drug abuse and misuse using the Researched Abuse Diversion and Addiction-related Surveillance (RADARS((R))) System. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry. 2013;52:196–204.e192. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2012.11.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

