Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Antibacterial Mechanism of Limonene against Listeria monocytogenes
- PMID: 31861877
- PMCID: PMC6982812
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25010033
Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Antibacterial Mechanism of Limonene against Listeria monocytogenes
Abstract
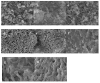
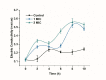
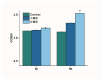
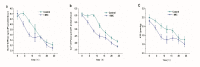
Limonene is a monoterpenoid compound, which is founded in a lot of plants' essential oils with good antibacterial activity against food-borne pathogens, but it has an ambiguous antimicrobial susceptibility and mechanism against Listeria monocytogenes (L. monocytogenes). In this study, the antimicrobial susceptibility of Limonene to L. monocytogenes was studied, and some new sights regarding its antibacterial mechanism were further explored. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) verified that limonene caused the destruction of the cell integrity and wall structure of L. monocytogenes. The increase in conductivity and the leakage of intracellular biomacromolecules (nucleic acids and proteins) confirmed that limonene had an obvious effect on cell membrane permeability. The results of Propidium Iodide (PI) fluorescence staining were consistent with the results of the conductivity measurements. This indicated that limonene treatment caused damage to the L. monocytogenes cell membrane. Furthermore, the decrease in ATP content, ATPase (Na+K+-ATPase, Ca2+-ATPase) activity and respiratory chain complex activity indicated that limonene could hinder ATP synthesis by inhibiting the activity of the respiratory complex and ATPase. Finally, differential expression of proteins in the respiratory chain confirmed that limonene affected respiration and energy metabolism by inhibiting the function of the respiratory chain complex.
Keywords: ATP; ATPase; Limonene; antibacterial mechanism; membrane damage; nucleic acid; protein; respiratory complexes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Strategic approach of multifaceted antibacterial mechanism of limonene traced in Escherichia coli.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 5;11(1):13816. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92843-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34226573 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Action of Osthole against Listeria monocytogenes.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 May 15;72(19):10853-10861. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c07931. Epub 2024 May 6. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38708871
-
Antimicrobial activity of gaseous Citrus limon var pompia leaf essential oil against Listeria monocytogenes on ricotta salata cheese.Food Microbiol. 2020 May;87:103386. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2019.103386. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Food Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31948627
-
Antimicrobial effects of sodium metasilicate against Listeria monocytogenes.Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2012 Sep;9(9):822-8. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2012.1207. Epub 2012 Aug 13. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2012. PMID: 22889042
-
Encapsulated Limonene: A Pleasant Lemon-Like Aroma with Promising Application in the Agri-Food Industry. A Review.Molecules. 2020 Jun 3;25(11):2598. doi: 10.3390/molecules25112598. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32503168 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chemical Profiling and Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, Cytotoxic, Analgesic, and Antidiarrheal Activities from the Seeds of Commonly Available Red Grape (Vitis vinifera L.).Nutr Metab Insights. 2024 Sep 18;17:11786388241275100. doi: 10.1177/11786388241275100. eCollection 2024. Nutr Metab Insights. 2024. PMID: 39315363 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidation of Phytochemical Content of Cupressus macrocarpa Leaves: In Vitro and In Vivo Antibacterial Effect against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Jul 22;10(8):890. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10080890. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34438940 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Activity and Mechanisms of Punicalagin against Vibrio parahaemolyticus.Foods. 2024 Apr 28;13(9):1366. doi: 10.3390/foods13091366. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38731737 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic antibacterial and antibiofilm effects of ultrasound and MEL-A against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Ultrason Sonochem. 2021 Apr;72:105452. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105452. Epub 2020 Dec 27. Ultrason Sonochem. 2021. PMID: 33388695 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Activity of Essential Oils from Clove and Elsholtzia Plants Against Common Pathogens of Bovine Mastitis, Antioxidant Activity, and Toxicity to Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells.Curr Microbiol. 2025 Jul 2;82(8):359. doi: 10.1007/s00284-025-04333-8. Curr Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40603548
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

