Fumagillin, a Mycotoxin of Aspergillus fumigatus: Biosynthesis, Biological Activities, Detection, and Applications
- PMID: 31861936
- PMCID: PMC7020470
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins12010007
Fumagillin, a Mycotoxin of Aspergillus fumigatus: Biosynthesis, Biological Activities, Detection, and Applications
Abstract
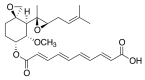
Fumagillin is a mycotoxin produced, above all, by the saprophytic filamentous fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. This mold is an opportunistic pathogen that can cause invasive aspergillosis, a disease that has high mortality rates linked to it. Its ability to adapt to environmental stresses through the production of secondary metabolites, including several mycotoxins (gliotoxin, fumagillin, pseurotin A, etc.) also seem to play an important role in causing these infections. Since the discovery of the A. fumigatus fumagillin in 1949, many studies have focused on this toxin and in this review we gather all the information currently available. First of all, the structural characteristics of this mycotoxin and the different methods developed for its determination are given in detail. Then, the biosynthetic gene cluster and the metabolic pathway involved in its production and regulation are explained. The activity of fumagillin on its target, the methionine aminopeptidase type 2 (MetAP2) enzyme, and the effects of blocking this enzyme in the host are also described. Finally, the applications that this toxin and its derivatives have in different fields, such as the treatment of cancer and its microsporicidal activity in the treatment of honeybee hive infections with Nosema spp., are reviewed. Therefore, this work offers a complete review of all the information currently related to the fumagillin mycotoxin secreted by A. fumigatus, important because of its role in the fungal infection process but also because it has many other applications, notably in beekeeping, the treatment of infectious diseases, and in oncology.
Keywords: Aspergillus fumigatus; MetAP2 enzyme; cancer treatment; chemical detection; fumagillin; honeybee hive infections.; metabolic pathway and regulation; microsporicidal activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Fumagillin: an overview of recent scientific advances and their significance for apiculture.J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Apr 2;62(13):2728-37. doi: 10.1021/jf4055374. Epub 2014 Mar 21. J Agric Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 24621007 Review.
-
A possible role for fumagillin in cellular damage during host infection by Aspergillus fumigatus.Virulence. 2018;9(1):1548-1561. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2018.1526528. Virulence. 2018. PMID: 30251593 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of neutrophil function following exposure to the Aspergillus fumigatus toxin fumagillin.J Med Microbiol. 2010 Jun;59(Pt 6):625-633. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.018192-0. Epub 2010 Mar 4. J Med Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20203215
-
Fist report on fumagillin production by Aspergillus fumigatus sensu stricto gliotoxigenic strains recovered from raw cow milk and clinical samples in Argentina.Rev Argent Microbiol. 2022 Jul-Sep;54(3):243-246. doi: 10.1016/j.ram.2022.03.003. Epub 2022 May 30. Rev Argent Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35654655
-
[On chance discovery in rational drug design. Aspergillus fumigatus and angiogenesis].Pharm Unserer Zeit. 2007;36(6):450-1. doi: 10.1002/pauz.200700242. Pharm Unserer Zeit. 2007. PMID: 17957690 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Identification and subcellular localization analysis of membrane protein Ycf 1 in the microsporidian Nosema bombycis.PeerJ. 2022 Jul 8;10:e13530. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13530. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35833014 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics approaches to understand pathogenicity during potato early blight disease caused by Alternaria solani.Front Microbiol. 2024 Mar 11;15:1357579. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1357579. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38529180 Free PMC article.
-
Editing gliA, gliP and gliZ of Aspergillus fumigatus Using CRISPR/Cas System Renders Fungus Incapable to Produce Gliotoxin.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Apr 4. doi: 10.1007/s12033-025-01429-1. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40186064
-
Fungal profile, levels of aflatoxin M1, exposure, and the risk characterization of local cheese 'wagashi' consumed in the Ho Municipality, Volta Region, Ghana.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Jan 17;12:186-199. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.01.009. eCollection 2024 Jun. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38313814 Free PMC article.
-
Managing Microbiota Activity of Apis mellifera with Probiotic (Bactocell®) and Antimicrobial (Fumidil B®) Treatments: Effects on Spring Colony Strength.Microorganisms. 2024 Jun 6;12(6):1154. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12061154. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38930537 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

