Marker-Assisted Gene Pyramiding and the Reliability of Using SNP Markers Located in the Recombination Suppressed Regions of Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.)
- PMID: 31861950
- PMCID: PMC7016752
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11010010
Marker-Assisted Gene Pyramiding and the Reliability of Using SNP Markers Located in the Recombination Suppressed Regions of Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.)
Abstract
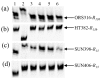
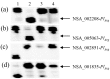
Rust caused by the fungus Puccinia helianthi and downy mildew (DM) caused by the obligate pathogen Plasmopara halstedii are two of the most globally important sunflower diseases. Resistance to rust and DM is controlled by race-specific single dominant genes. The present study aimed at pyramiding rust resistance genes combined with a DM resistance gene, using molecular markers. Four rust resistant lines, HA-R3 (carrying the R4 gene), HA-R2 (R5), HA-R8 (R15), and RHA 397 (R13b), were each crossed with a common line, RHA 464, carrying a rust gene R12 and a DM gene PlArg. An additional cross was made between HA-R8 and RHA 397. Co-dominant simple sequence repeat (SSR) and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers linked to the target genes were used to discriminate between homozygotes and heterozygotes in F2 populations. Five pyramids with different combinations of rust resistance genes were selected in the homozygous condition through marker-assisted selection, and three of them were combined with a DM resistance gene PlArg: R4/R12/PlArg, R5/R12/PlArg, R13b/R12/PlArg, R15/R12, and R13b/R15. The pyramiding lines with the stacking of two rust and one DM genes were resistant to all known races of North American sunflower rust and all known races of the pathogen causing DM, potentially providing multiple and durable resistance to both rust and DM. A cluster of 12 SNP markers spanning a region of 34.5 Mb on chromosome 1, which co-segregate with PlArg, were tested in four populations. Use of those markers, located in a recombination suppressed region in marker selection, is discussed.
Keywords: downy mildew; gene pyramiding; resistance; rust; sunflower.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Development and dissection of diagnostic SNP markers for the downy mildew resistance genes Pl Arg and Pl 8 and maker-assisted gene pyramiding in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.).Mol Genet Genomics. 2017 Jun;292(3):551-563. doi: 10.1007/s00438-017-1290-8. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Mol Genet Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28160079
-
Genetic mapping of rust resistance genes in confection sunflower line HA-R6 and oilseed line RHA 397.Theor Appl Genet. 2013 Aug;126(8):2039-49. doi: 10.1007/s00122-013-2116-7. Epub 2013 May 30. Theor Appl Genet. 2013. PMID: 23719761
-
Molecular tagging of a novel rust resistance gene R(12) in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2013 Jan;126(1):93-9. doi: 10.1007/s00122-012-1962-z. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Theor Appl Genet. 2013. PMID: 22907633
-
Relocation of a rust resistance gene R 2 and its marker-assisted gene pyramiding in confection sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2015 Mar;128(3):477-88. doi: 10.1007/s00122-014-2446-0. Epub 2015 Jan 11. Theor Appl Genet. 2015. PMID: 25575836
-
High-throughput genotyping-by-sequencing facilitates molecular tagging of a novel rust resistance gene, R 15 , in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2018 Jul;131(7):1423-1432. doi: 10.1007/s00122-018-3087-5. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Theor Appl Genet. 2018. PMID: 29564500
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Black Phosphorus Nanosheets Elicit Neutrophil Response for Enhanced Tumor Suppression.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Apr;12(14):e2414779. doi: 10.1002/advs.202414779. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39840467 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome profile of pecan scab resistant and susceptible trees from a pecan provenance collection.BMC Genomics. 2024 Feb 15;25(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10010-0. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38355402 Free PMC article.
-
Update on Cancer Screening in Children with Syndromes of Bone Lesions, Hereditary Leiomyomatosis and Renal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome, and Other Rare Syndromes.Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Feb 3;31(3):457-465. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-2171. Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39601780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Insight into Disease Resistance Gene Clusters by Using Sequencing-Based Fine Mapping in Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 23;23(17):9516. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179516. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36076914 Free PMC article.
-
Breeding and Genomic Approaches towards Development of Fusarium Wilt Resistance in Chickpea.Life (Basel). 2023 Apr 11;13(4):988. doi: 10.3390/life13040988. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37109518 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vear F. Breeding disease-resistant sunflowers. CAB Rev. 2017;12:1–11. doi: 10.1079/PAVSNNR201712035. - DOI
-
- Putt E.D., Sackston W.E. Studies on sunflower rust. I. Some sources of rust resistance. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1957;37:43–54. doi: 10.4141/cjps57-005. - DOI
-
- Putt E.D., Sackston W.E. Studies on sunflower rust. IV. Two genes, R1 and R2 for resistance in the host. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1963;43:490–496. doi: 10.4141/cjps63-100. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

