Effects of different doses of magnesium sulfate on pneumoperitoneum-related hemodynamic changes in patients undergoing gastrointestinal laparoscopy: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial
- PMID: 31862004
- PMCID: PMC6925413
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-019-0886-4
Effects of different doses of magnesium sulfate on pneumoperitoneum-related hemodynamic changes in patients undergoing gastrointestinal laparoscopy: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial
Abstract
Background: The infusion of magnesium sulfate is well known to reduce arterial pressure and attenuate hemodynamic response to pneumoperitoneum. This study aimed to investigate whether different doses of magnesium sulfate can effectively attenuate the pneumoperitoneum-related hemodynamic changes and the release of vasopressin in patients undergoing laparoscopic gastrointestinal surgery.
Methods: Sixty-nine patients undergoing laparoscopic partial gastrectomy were randomized into three groups: group L received magnesium sulfate 30 mg/kg loading dose and 15 mg/kg/h continuous maintenance infusion for 1 h; group H received magnesium sulfate 50 mg/kg followed by 30 mg/kg/h for 1 h; and group S (control group) received same volume 0.9% saline infusion, immediately before the induction of pneumoperitoneum. Systemic vascular resistance (SVR), cardiac output (CO), mean arterial pressure (MAP), heart rate (HR), central venous pressure (CVP), serum vasopressin and magnesium concentrations were measured. The extubation time, visual analogue scale were also assessed. The primary outcome is the difference in SVR between different groups. The secondary outcome is the differences of other indicators between groups, such as CO, MAP, HR, CVP, vasopressin and postoperative pain score.
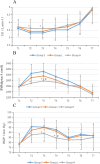
Results: Pneumoperitoneum instantly resulted in a significant reduction of cardiac output and an increase in mean arterial pressure, systemic vascular resistance, central venous pressure and heart rate in the control group (P < 0.01). The mean arterial pressure (T2 - T4), systemic vascular resistance (T2 - T3), central venous pressure(T3-T5) and the level of serum vasopressin were significantly lower (P < 0.05) and the cardiac output (T2 - T3) was significantly higher (P < 0.05) in group H than those in the control group. The mean arterial pressure (T4), systemic vascular resistance (T2), and central venous pressure(T3-T4) were significantly lower in group H than those in group L (P < 0.05). Furthermore, the visual analog scales at 5 min and 20 min, the level of vasopressin, and the dose of remifentanil were significantly decreased in group H compared to the control group and group L (P < 0.01).
Conclusion: Magnesium sulfate could safely and effectively attenuate the pneumoperitoneum-related hemodynamic instability during gastrointestinal laparoscopy and improve postoperative pain at serum magnesium concentrations above 2 mmol/L.
Trial registration: The study was retrospectively registered at Chinese Clinical Trial Registry; the registration number is ChiCTR-IPD-17011145, principal investigator: D.Y. Q., date of registration: April 13, 2017.
Keywords: Magnesium sulfate; Pneumoperitoneum; Systemic vascular resistance; Vasopressin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[The role of magnesium sulfate in providing hemodynamic stability in patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery: a prospective randomized controlled study].Pan Afr Med J. 2024 Apr 29;47:215. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2024.47.215.41212. eCollection 2024. Pan Afr Med J. 2024. PMID: 39247774 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. French.
-
Magnesium sulphate attenuates arterial pressure increase during laparoscopic cholecystectomy.Br J Anaesth. 2009 Oct;103(4):484-9. doi: 10.1093/bja/aep196. Epub 2009 Jul 17. Br J Anaesth. 2009. PMID: 19617379 Clinical Trial.
-
Prospective, randomized and controlled trial on magnesium sulfate administration during laparoscopic gastrectomy: effects on surgical space conditions and recovery profiles.Surg Endosc. 2016 Nov;30(11):4976-4984. doi: 10.1007/s00464-016-4842-9. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Surg Endosc. 2016. PMID: 26969660 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of intravenous magnesium sulfate to attenuate hemodynamic changes in laparoscopic surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.JBI Evid Synth. 2021 Mar;19(3):578-603. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-D-19-00414. JBI Evid Synth. 2021. PMID: 33074990
-
The Impact of Intraoperative CO 2 Pneumoperitoneum Pressure in Gastrointestinal Surgery: A Systematic Review.Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2025 Apr 1;35(2):e1325. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0000000000001325. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2025. PMID: 39925242 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prevention of Shivering Post Subarachnoid Block: Comparison between Different Doses of Intravenous Magnesium Sulphate.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Aug 3;58(8):1046. doi: 10.3390/medicina58081046. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36013512 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Intravenous Injection of Magnesium Sulphate on Intraoperative End-Tidal CO2 Level and Postoperative Pain in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy.Anesth Pain Med. 2023 Dec 31;13(6):e135189. doi: 10.5812/aapm-135189. eCollection 2023 Dec. Anesth Pain Med. 2023. PMID: 38721443 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant Analgesics in Acute Pain - Evaluation of Efficacy.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024 Sep;28(9):843-852. doi: 10.1007/s11916-024-01276-w. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024. PMID: 38865074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Relieving Effects of a Polyherb-Based Dietary Supplement ColonVita on Gastrointestinal Quality of Life Index (GIQLI) in Older Adults with Chronic Gastrointestinal Symptoms Are Influenced by Age and Cardiovascular Disease: A 12-Week Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Sep 10;2021:6653550. doi: 10.1155/2021/6653550. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34539805 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of intra-operative magnesium sulfate infusion on orthognathic surgery: A prospective and randomized controlled trial.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 25;10(9):e30342. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30342. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38707412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Puri GD, Marudhachalam KS, Chari P. The effect of magnesium sulphate on hemodynamics and its efficacy in attenuating the response to endotracheal intubation in patients with coronary artery disease. Anesth Analg. 1998;87:808–811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

