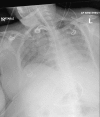
Sertraline-induced hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- PMID: 31862812
- PMCID: PMC6936525
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2019-230724
Sertraline-induced hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Corrected and republished in
-
Republished: Sertraline-induced hypersensitivity pneumonitis.Drug Ther Bull. 2020 May;58(5):75-79. doi: 10.1136/dtb.2019.230724rep. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Drug Ther Bull. 2020. PMID: 32188684 No abstract available.
Abstract
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP), also known as extrinsic allergic alveolitis, is a granulomatous, non-IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reaction of the alveoli and distal bronchioles presenting as an acute, subacute or chronic condition. It is most commonly associated with exposure to extrinsic allergens (eg, avian dust, mould and tobacco) and medications including antiarrhythmics (eg, amiodarone), cytotoxics (eg, methotrexate) and antiepileptics (eg, carbamazepine). Individuals diagnosed with this condition can present with severe hypoxia and respiratory failure. The fundamental principle of management is to remove the causative allergen. Evidence implicating selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors as a causative agent is limited, and this case report describes a rare clinical presentation of HP associated with sertraline, how it was diagnosed and subsequently treated. It is anticipated that raising awareness of this interaction will assist multidisciplinary teams, managing patients diagnosed with HP, to be more cognisant of sertraline as being an aetiological factor for this condition.
Keywords: Unwanted effects / adverse reactions; adult intensive care; interstitial lung disease; psychiatry (drugs and medicines); respiratory medicine.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2019. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Hypersensitivity pneumonitis presenting as acute respiratory distress syndrome].Rev Mal Respir. 2019 Jun;36(6):747-751. doi: 10.1016/j.rmr.2017.12.006. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Rev Mal Respir. 2019. PMID: 31202600 French.
-
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis in a Pediatric Patient.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2021 Jun;31(6):735-736. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2021.06.735. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2021. PMID: 34102793
-
Aripiprazole-induced hypersensitivity pneumonitis.BMJ Case Rep. 2017 May 9;2017:bcr2017219929. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-219929. BMJ Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28487307 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in hypersensitivity pneumonitis.Chest. 2012 Jul;142(1):208-217. doi: 10.1378/chest.11-2479. Chest. 2012. PMID: 22796841 Review.
-
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: a noninfectious granulomatosis.Semin Respir Infect. 1995 Jun;10(2):96-106. Semin Respir Infect. 1995. PMID: 7569404 Review.
Cited by
-
Sertraline-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: A case series and Literature Review.Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2021;38(3):e2021027. doi: 10.36141/svdld.v38i3.11363. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2021. PMID: 34744423 Free PMC article.
-
Sertraline as a rare cause of interstitial lung disease.Oxf Med Case Reports. 2021 Apr 28;2021(4):omab014. doi: 10.1093/omcr/omab014. eCollection 2021 Apr. Oxf Med Case Reports. 2021. PMID: 33948187 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacomicrobiology of Methotrexate in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Gut Microbiome as Predictor of Therapeutic Response.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 16;12:789334. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.789334. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34975886 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xue-Fen C, Peng S, Li J, et al. . Ijcep.com, 2018. Available: http://www.ijcep.com/files/ijcep0018676.pdf [Accessed 29 Nov 2018].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous