Effectiveness of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockade on Residual Kidney Function and Peritoneal Membrane Function in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: A Network Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 31862905
- PMCID: PMC6925258
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-55561-5
Effectiveness of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockade on Residual Kidney Function and Peritoneal Membrane Function in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: A Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
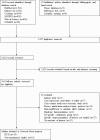
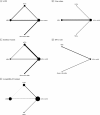
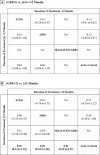
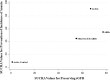
We performed a network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and non-randomised studies in adult peritoneal dialysis patients to evaluate the effects of specific renin-angiotensin aldosterone systems (RAAS) blockade classes on residual kidney function and peritoneal membrane function. Key outcome parameters included the following: residual glomerular filtration rate (rGFR), urine volume, anuria, dialysate-to-plasma creatinine ratio (D/P Cr), and acceptability of treatment. Indirect treatment effects were compared using random-effects model. Pooled standardised mean differences (SMDs) and odd ratios (ORs) were estimated with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). We identified 10 RCTs (n = 484) and 10 non-randomised studies (n = 3,305). Regarding changes in rGFR, RAAS blockade with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) were more efficacious than active control (SMD 0.55 [0.06-1.04] and 0.62 [0.19-1.04], respectively) with the protective effect on rGFR observed only after usage ≥12 months, and no differences among ACEIs and ARBs. Compared with active control, only ACEIs showed a significantly decreased risk of anuria (OR 0.62 [0.41-0.95]). No difference among treatments for urine volume and acceptability of treatment were observed, whereas evidence for D/P Cr is inconclusive. The small number of randomised studies and differences in outcome definitions used may limit the quality of the evidence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Renin-angiotensin system blockers and residual kidney function loss in patients initiating peritoneal dialysis: an observational cohort study.BMC Nephrol. 2017 Jun 17;18(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s12882-017-0616-4. BMC Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28623899 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment with angiotensin II inhibitors and residual renal function in peritoneal dialysis patients.Perit Dial Int. 2011 Jan-Feb;31(1):53-9. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2009.00088. Epub 2010 Jun 3. Perit Dial Int. 2011. PMID: 20522672
-
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade and arterial stiffness in renal transplant recipients - a cross-sectional prospective observational clinical study.Acta Biochim Pol. 2020 Dec 17;67(4):613-622. doi: 10.18388/abp.2020_5490. Acta Biochim Pol. 2020. PMID: 33332078
-
Effects of ACEIs and ARBs on the Residual Renal Function in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Sep 23;2020:6762029. doi: 10.1155/2020/6762029. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33029520 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers on cardiovascular events and residual renal function in dialysis patients: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.BMC Nephrol. 2017 Jun 30;18(1):206. doi: 10.1186/s12882-017-0605-7. BMC Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28666408 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Renal anemia and hyporesponsiveness to ESA for preservation of residual kidney function in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 21;15(1):2689. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87456-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39838061 Free PMC article.
-
Peritoneal and renal DKK3 clearance in peritoneal dialysis.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Aug 23;25(1):268. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03715-7. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39179976 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers on all-cause mortality, cardiovascular death, and cardiovascular events among peritoneal dialysis patients: A protocol for systematic review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Apr;99(17):e19767. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019767. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32332616 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17A as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis.Biomolecules. 2020 Sep 24;10(10):1361. doi: 10.3390/biom10101361. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32987705 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Williams, J. D., Craig, K. J., von Ruhland, C., Topley, N. & Williams, G. T. The natural course of peritoneal membrane biology during peritoneal dialysis. Kidney Int Suppl. S43–49 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Bargman JM, Thorpe KE, Churchill DN. Relative contribution of residual renal function and peritoneal clearance to adequacy of dialysis: a reanalysis of the CANUSA study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12:2158–2162. - PubMed
-
- Termorshuizen F, et al. The relative importance of residual renal function compared with peritoneal clearance for patient survival and quality of life: an analysis of the Netherlands Cooperative Study on the Adequacy of Dialysis (NECOSAD)-2. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41:1293–1302. doi: 10.1016/S0272-6386(03)00362-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

