Farnesoid X receptor and bile acids regulate vitamin A storage
- PMID: 31862954
- PMCID: PMC6925179
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-55988-w
Farnesoid X receptor and bile acids regulate vitamin A storage
Abstract
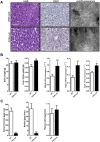
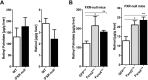
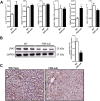
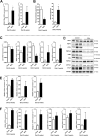
The nuclear receptor Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) is activated by bile acids and controls multiple metabolic processes, including bile acid, lipid, carbohydrate, amino acid and energy metabolism. Vitamin A is needed for proper metabolic and immune control and requires bile acids for efficient intestinal absorption and storage in the liver. Here, we analyzed whether FXR regulates vitamin A metabolism. Compared to control animals, FXR-null mice showed strongly reduced (>90%) hepatic levels of retinol and retinyl palmitate and a significant reduction in lecithin retinol acyltransferase (LRAT), the enzyme responsible for hepatic vitamin A storage. Hepatic reintroduction of FXR in FXR-null mice induced vitamin A storage in the liver. Hepatic vitamin A levels were normal in intestine-specific FXR-null mice. Obeticholic acid (OCA, 3 weeks) treatment rapidly reduced (>60%) hepatic retinyl palmitate levels in mice, concurrent with strongly increased retinol levels (>5-fold). Similar, but milder effects were observed in cholic acid (12 weeks)-treated mice. OCA did not change hepatic LRAT protein levels, but strongly reduced all enzymes involved in hepatic retinyl ester hydrolysis, involving mostly post-transcriptional mechanisms. In conclusion, vitamin A metabolism in the mouse liver heavily depends on the FXR and FXR-targeted therapies may be prone to cause vitamin A-related pathologies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors certify that they have NO affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials described in this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Farnesoid X Receptor Activation Promotes Hepatic Amino Acid Catabolism and Ammonium Clearance in Mice.Gastroenterology. 2017 May;152(6):1462-1476.e10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.01.014. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Gastroenterology. 2017. PMID: 28130067
-
Low retinol levels differentially modulate bile salt-induced expression of human and mouse hepatic bile salt transporters.Hepatology. 2009 Jan;49(1):151-9. doi: 10.1002/hep.22661. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19111018
-
Comparative potency of obeticholic acid and natural bile acids on FXR in hepatic and intestinal in vitro cell models.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2017 Dec;5(6):e00368. doi: 10.1002/prp2.368. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2017. PMID: 29226620 Free PMC article.
-
A Short Review on Obeticholic Acid: An Effective Modulator of Farnesoid X Receptor.Curr Rev Clin Exp Pharmacol. 2024;19(3):225-233. doi: 10.2174/0127724328239536230919070001. Curr Rev Clin Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38708917 Review.
-
The role of farnesoid X receptor in metabolic diseases, and gastrointestinal and liver cancer.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 May;18(5):335-347. doi: 10.1038/s41575-020-00404-2. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33568795 Review.
Cited by
-
Retinoid metabolism: new insights.J Mol Endocrinol. 2022 Oct 11;69(4):T37-T49. doi: 10.1530/JME-22-0082. Print 2022 Nov 1. J Mol Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35900851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbiota-Testis Axis: FMT Mitigates High-Fat Diet-Diminished Male Fertility via Improving Systemic and Testicular Metabolome.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0002822. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00028-22. Epub 2022 Apr 21. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35446112 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acid regulates pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (Pdk4) to modulate fuel utilization in the adult heart: Insights from wild-type and β-carotene 9',10' oxygenase knockout mice.FASEB J. 2022 Sep;36(9):e22513. doi: 10.1096/fj.202101910RR. FASEB J. 2022. PMID: 36004605 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Pharmacological Mechanisms of Eleutheroside E Against Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Through UPLC-Q/TOF-MS-Based Metabolomics.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Aug 26;11:1316. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01316. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32982736 Free PMC article.
-
A retinoic acid receptor β2 agonist attenuates transcriptome and metabolome changes underlying nonalcohol-associated fatty liver disease.J Biol Chem. 2021 Dec;297(6):101331. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101331. Epub 2021 Oct 21. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34688661 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

