Dual microglia effects on blood brain barrier permeability induced by systemic inflammation
- PMID: 31862977
- PMCID: PMC6925219
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-13812-z
Dual microglia effects on blood brain barrier permeability induced by systemic inflammation
Abstract
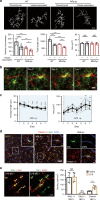
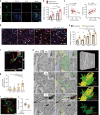
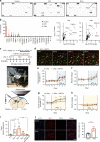
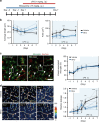
Microglia survey brain parenchyma, responding to injury and infections. Microglia also respond to systemic disease, but the role of blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity in this process remains unclear. Using simultaneous in vivo imaging, we demonstrated that systemic inflammation induces CCR5-dependent migration of brain resident microglia to the cerebral vasculature. Vessel-associated microglia initially maintain BBB integrity via expression of the tight-junction protein Claudin-5 and make physical contact with endothelial cells. During sustained inflammation, microglia phagocytose astrocytic end-feet and impair BBB function. Our results show microglia play a dual role in maintaining BBB integrity with implications for elucidating how systemic immune-activation impacts neural functions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

