Targeting interleukin 4 receptor α: A new approach to the treatment of cutaneous autoimmune bullous diseases?
- PMID: 31863534
- PMCID: PMC7154653
- DOI: 10.1111/dth.13190
Targeting interleukin 4 receptor α: A new approach to the treatment of cutaneous autoimmune bullous diseases?
Abstract
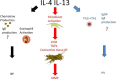
Bullous pemphigoid, mucous membrane pemphigoid, and pemphigus vulgaris are different cutaneous autoimmune blistering diseases, with complex pathogenic mechanisms. In all of them, a type-2 response is thought to have a central role. Interleukin 4 and Interleukin 13 are crucial cytokines in type-2 response. Treatment of these conditions is often challenging. Dupilumab, a recombinant fully human IgG4 monoclonal antibody with binding specificity to human interleukin-4 receptor IL-4Rα, has the potential to inhibit both IL-4 and IL-13. We propose IL-4Rα as a theoretical drug target for cutaneous autoimmune bullous diseases.
Keywords: blistering diseases; bullous pemphigoid; dupilumab; mucous membrane pemphigoid; pemphigus vulgaris.
© 2019 The Authors. Dermatologic Therapy published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aoudjehane, L. , Pissaia, A., Jr. , Scatton, O. , Podevin, P. , Massault, P. P. , Chouzenoux, S. , … Conti, F. (2008). Interleukin‐4 induces the activation and collagen production of cultured human intrahepatic fibroblasts via the stat‐6 pathway. Laboratory Investigation, 88, 973–985. - PubMed
-
- Bailey, J. R. , Bland, P. W. , Tarlton, J. F. , Peters, I. , Moorghen, M. , Sylvester, P. A. , … Whiting, C. V. (2012). IL‐13 promotes collagen accumulation in Crohn's disease fibrosis by down‐regulation of fibroblast MMP synthesis: A role for innate lymphoid cells? PLoS One, 7, e52332. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bellini, A. , Marini, M. A. , Bianchetti, L. , Barczyk, M. , Schmidt, M. , & Mattoli, S. (2012). Interleukin (IL)‐4, IL‐13, and IL‐17A differentially affect the profibrotic and proinflammatory functions of fibrocytes from asthmatic patients. Mucosal Immunology, 5, 140–149. - PubMed
-
- Belperio, J. A. , Dy, M. , Burdick, M. D. , Xue, Y. Y. , Li, K. , Elias, J. A. , & Keane, M. P. (2002). Interaction of IL‐13 and C10 in the pathogenesis of bleomycin‐induced pulmonary fibrosis. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology, 27, 419–427. - PubMed
-
- Bernard, P. , & Antonicelli, F. (2017). Bullous pemphigoid: A review of its diagnosis, associations and treatment. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology, 18, 513–528. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical