Circular RNA circ-CMPK1 contributes to cell proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer by elevating cyclin D1 via sponging miR-302e
- PMID: 31863641
- PMCID: PMC7005605
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.999
Circular RNA circ-CMPK1 contributes to cell proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer by elevating cyclin D1 via sponging miR-302e
Abstract
Background: It is well recognized that competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) regulatory network is linked to the development and progression of cancer, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Herein, we aimed to explore the functional role of circ-CMPK1/miR-302e/cyclin D1 ceRNA signaling in NSCLC.
Methods: GEO database (GSE102287) was utilized to screen differentially expressed miRNAs in NSCLC. Quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) and western blotting assays were used to determine gene expression. Cell proliferation analysis was performed with Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and cell cycle assays. Luciferase reporter and RNA pull-down assays were conducted to identify the interaction among circ-CMPK1, miR-302e, and cyclin D1. Xenograft tumor model was established to evaluate the role of circ-CMPK1/miR-302e/cyclin D1 axis in vivo.
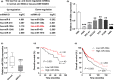
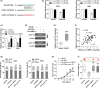
Results: miR-302e expression was significantly down-regulated in NSCLC cell lines and tissues and its decrease was closely associated with aggressive clinicopathological features and unfavorable outcome. Overexpression and knockdown of miR-302e obviously retarded and enhanced the growth of NSCLC, respectively. Furthermore, we found that miR-302 was sponged by circular RNA CMPK1 (circ-CMPK1, hsa_circ_0012384), which was remarkably up-regulated in NSCLC and predicted poor prognosis. Circ-CMPK1 was capable to promote NSCLC cells proliferation by increasing the expression of cyclin D1 via inhibiting miR-302 activity. Moreover the miR-302e-mediated tumor inhibition could be effectively counteracted by ectopic expression of circ-CMPK1 or cyclin D1 both in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrate for the first time that circ-CMPK1/miR-302e/cyclin D1 signaling plays an essential regulatory role in NSCLC and targeting this axis may be an efficacious avenue for treatment of NSCLC patients.
Keywords: NSCLC; biomarker; ceRNA; circular RNA; microRNA; proliferation.
© 2019 The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing financial interests to be declared.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

