Scavenging reactive oxygen species selectively inhibits M2 macrophage polarization and their pro-tumorigenic function in part, via Stat3 suppression
- PMID: 31863907
- PMCID: PMC10035558
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.12.018
Scavenging reactive oxygen species selectively inhibits M2 macrophage polarization and their pro-tumorigenic function in part, via Stat3 suppression
Abstract
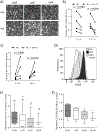
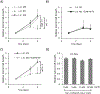
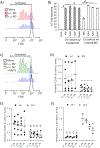
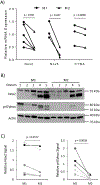
Tumor associated macrophages (TAM) enhance the aggressiveness of breast cancer via promoting cancer cell growth, metastasis, and suppression of the patient's immune system. These TAMs are polarized in breast cancer with features more closely resembling the pro-tumorigenic and immunosuppressive M2 type rather than the anti-tumor and pro-inflammatory M1 type. The goal of our study was to examine primary human monocyte-derived M1 and M2 macrophages for key redox differences and determine sensitivities of these macrophages to the redox-active drug, MnTE-2-PyP5+. This compound reduced levels of M2 markers and inhibited their ability to promote cancer cell growth and suppress T cell activation. The surface levels of the T cell suppressing molecule, PD-L2, were reduced by MnTE-2-PyP5+ in a dose-dependent manner. This study also examined key differences in ROS generation and scavenging between M1 and M2 macrophages. Our results indicate that M2 macrophages have lower levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lower production of extracellular hydrogen peroxide compared to the M1 macrophages. These differences are due in part to reduced expression levels of pro-oxidants, Nox2, Nox5, and the non-enzymatic members of the Nox complex, p22phox and p47phox, as well as higher levels of antioxidant enzymes, Cu/ZnSOD, Gpx1, and catalase. More importantly, we found that despite having lower ROS levels, M2 macrophages require ROS for proper polarization, as addition of hydrogen peroxide increased M2 markers. These TAM-like macrophages are also more sensitive to the ROS modulator and a pan-Nox inhibitor. Both MnTE-2-PyP5+ and DPI inhibited expression levels of M2 marker genes. We have further shown that this inhibition was partly mediated through a decrease in Stat3 activation during IL4-induced M2 polarization. Overall, this study reveals key redox differences between M1 and M2 primary human macrophages and that redox-active drugs can be used to inhibit the pro-tumor and immunosuppressive phenotype of TAM-like M2 macrophages. This study also provides rationale for combining MnTE-2-PyP5+ with immunotherapies.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Immunosuppression; ROS; SOD mimetics; Stat3; Tumor associated macrophages.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibition of STAT3 by 2-Methoxyestradiol suppresses M2 polarization and protumoral functions of macrophages in breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2024 Sep 10;24(1):1129. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12871-w. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39256694 Free PMC article.
-
Pyropia yezoensis glycoprotein promotes the M1 to M2 macrophage phenotypic switch via the STAT3 and STAT6 transcription factors.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Aug;38(2):666-74. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2656. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27353313
-
MnTE-2-PyP modulates thiol oxidation in a hydrogen peroxide-mediated manner in a human prostate cancer cell.Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 Dec;101:32-43. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.09.019. Epub 2016 Sep 24. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27671770 Free PMC article.
-
The Reactive Oxygen Species in Macrophage Polarization: Reflecting Its Dual Role in Progression and Treatment of Human Diseases.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:2795090. doi: 10.1155/2016/2795090. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 27143992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovitis.Front Immunol. 2022 May 19;13:867260. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.867260. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35663975 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Wound Healing versus Metastasis: Role of Oxidative Stress.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 2;10(11):2784. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112784. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36359304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-Dose Dexamethasone Manipulates the Tumor Microenvironment and Internal Metabolic Pathways in Anti-Tumor Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 7;21(5):1846. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051846. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32156004 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming the breast tumor immune microenvironment: cold-to-hot transition for enhanced immunotherapy.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Apr 25;44(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03394-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40281554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Demystifying the cGAS-STING pathway: precision regulation in the tumor immune microenvironment.Mol Cancer. 2025 Jun 12;24(1):178. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02380-0. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40506729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precise modulation and use of reactive oxygen species for immunotherapy.Sci Adv. 2024 May 17;10(20):eadl0479. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adl0479. Epub 2024 May 15. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38748805 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leek RD, et al., Association of Macrophage Infiltration with Angiogenesis and Prognosis in Invasive Breast Carcinoma. Cancer Research, 1996. 56(20): p. 4625–4629. - PubMed
-
- Bingle L, Brown NJ, and Lewis CE, The role of tumour-associated macrophages in tumour progression: implications for new anticancer therapies. J Pathol, 2002. 196(3): p. 254–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

