Effectiveness of Virtual Reality Eyeglasses as a Distraction Aid to Reduce Anxiety among 6-10-year-old Children Undergoing Dental Extraction Procedure
- PMID: 31866714
- PMCID: PMC6898869
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1640
Effectiveness of Virtual Reality Eyeglasses as a Distraction Aid to Reduce Anxiety among 6-10-year-old Children Undergoing Dental Extraction Procedure
Abstract
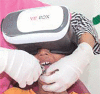
Introduction: Distraction is commonly used nonpharmacologic pain management technique by pedodontists to manage pain and anxiety. There are some new techniques which uses audiovideo stimulation and distract the patient by exposing him or her to three-dimensional videos. These techniques are referred to as virtual reality audiovisual systems. The aim is to evaluate the effectiveness of virtual reality eyeglasses as a distraction aid to reduce anxiety of children undergoing extraction procedure.
Objective: The aim of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of virtual reality eyeglasses as a distraction aid to reduce anxiety of children undergoing dental extraction procedure.
Materials and methods: Thirty children of age 6-10 years (n = 60) with bilateral carious primary molars indicated for extraction were randomly selected and divided into two groups of 30 each. The first one was group I (VR group) (n = 30) and group II (control group) (n = 30). Anxiety was measured by using Venham's picture test, pulse rate and oxygen saturation. Anxiety level between group I and group II was assessed using paired "t" test.
Results: The mean pulse rate values after extraction procedure in group I were 107.833 ± 1.356 and group II were 108.4 ± 0.927 respectively. The pulse rate values in intergroup comparison were found statistically significant p = 0.03.
Conclusion: The virtual reality used as a distraction technique improves the physiologic parameters of children aged 6-10 years but does not reduce the patient's self-reported anxiety according to Venham's picture test used.
How to cite this article: Koticha P, Katge F, et al. Effectiveness of Virtual Reality Eyeglasses as a Distraction Aid to Reduce Anxiety among 6-10-year-old Children Undergoing Dental Extraction Procedure. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent 2019;12(4):297-302.
Keywords: Audiovisual; Distraction; Oxygen saturation; Pulse rate; Venham picture test; Virtual reality eyeglasses.
Copyright © 2019; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None
Figures



References
-
- Bankole OO, Aderinokun GA, et al. Maternal and child's anxiety—effect on child's behaviour at dental appointments and treatments. Afr J Med Med Sci. 2002;31:349–352. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
