The Magnitude of Postconvulsive Leukocytosis Mirrors the Severity of Periconvulsive Respiratory Compromise: A Single Center Retrospective Study
- PMID: 31866936
- PMCID: PMC6910016
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2019.01291
The Magnitude of Postconvulsive Leukocytosis Mirrors the Severity of Periconvulsive Respiratory Compromise: A Single Center Retrospective Study
Abstract
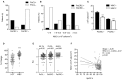
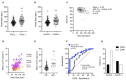
Background: Generalized epileptic convulsions frequently exhibit transient respiratory symptoms and non-infectious leukocytosis. While these peri-ictal effects appear to arise independently from one another, the possibility that they stem from a common ictal pathophysiological response has yet to be explored. We aimed to investigate whether peri-ictal respiratory symptoms and postictal leukocytosis coexist. Methods: We performed a single center retrospective chart review of 446 patients brought to our emergency department between January 1, 2017 and August 23, 2018 for the care of generalized epileptic convulsions with or without status epilepticus. We included 152 patients who were stratified based on the presence (PeCRC+) or absence (PeCRC-) of overt periconvulsive respiratory compromise (PeCRC). In addition, patients were stratified based on the presence or absence of postconvulsive leukocytosis (PoCL), defined as an initial postconvulsive white blood cell (WBC) count ≥ 11,000 cells/mm3. Triage vital signs, and chest x ray (CXR) abnormalities were also examined. Results: Overt PeCRC was observed in 31.6% of patients, 43% of whom required emergent endotracheal intubations. PoCL was observed in 37.5% of patients, and was more likely to occur in PeCRC+ than in PeCRC- patients (79.2 vs. 18.2%; OR = 17.0; 95% CI = 7.2-40.9; p < 0.001). Notably, the magnitude of PoCL was proportional to the severity of PeCRC, as the postconvulsive WBC count demonstrated a negative correlation with triage hemoglobin oxygen saturation (R = -0.22; p < 0.01; CI = -0.48 to -0.07). Moreover, a receiver operating characteristic analysis of the WBC count's performance as predictor of endotracheal intubation reached a significant area under the curve value of 0.81 (95% CI = 0.71-0.90; p < 0.001). Finally, PeCRC+ patients demonstrated frequent CXR abnormalities, and their postconvulsive WBC counts correlated directly with triage heart rate (R = 0.53; p < 0.001). Conclusion: Our data support the existence of an ictal pathophysiological response, which induces proportional degrees of PoCL and PeCRC. We suggest this response is at least partially propelled by systemic catecholamines.
Keywords: catecholamines; generalized epileptic convulsions; leukocytosis; neurogenic pulmonary edema; pulmonary edema; respiratory failure.
Copyright © 2019 Vega, Emmady, Roels, Conforti, Ramirez and Dorak.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biomarkers for SUDEP: Are We There Yet?Epilepsy Curr. 2019 Jul-Aug;19(4):231-233. doi: 10.1177/1535759719855948. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Epilepsy Curr. 2019. PMID: 31189384 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Value of Leukocytosis for Infectious Complications After Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy.Urology. 2015 Jul;86(1):25-9. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2015.04.026. Urology. 2015. PMID: 26142577
-
Leukocytosis is common after orthognathic surgery: A retrospective study.J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019 Nov;120(5):443-449. doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2018.12.013. Epub 2019 Jan 1. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019. PMID: 30609385
-
Significance of leukocytosis after cardiac device implantation.Am J Cardiol. 2013 Jun 1;111(11):1608-12. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.01.334. Epub 2013 Mar 20. Am J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23523060
-
Prognostic value of leukocytosis in acute coronary syndromes: the cinderella of the inflammatory markers.Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(18):2113-8. doi: 10.2174/092986706777935221. Curr Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16918341 Review.
Cited by
-
Hiding in plain sight? A review of post-convulsive leukocyte elevations.Front Neurol. 2022 Nov 2;13:1021042. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1021042. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36408527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Blood C Reactive Protein (CRP) and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) Utility in Canine Epilepsy.Vet Sci. 2024 Sep 4;11(9):408. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11090408. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39330787 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent cerebellar ischemic infarctions and stereotyped peri-ictal sympathetic responses in a near-SUDEP patient with cardiovascular risk factors.Epilepsy Behav Rep. 2023 May 11;23:100605. doi: 10.1016/j.ebr.2023.100605. eCollection 2023. Epilepsy Behav Rep. 2023. PMID: 37332897 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

