As4S4 Exhibits Good Killing Effect on Multiple Myeloma Cells Via Repressing SOCS1 Methylation-Mediated JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 31868118
- PMCID: PMC6928533
- DOI: 10.1177/1533033819896806
As4S4 Exhibits Good Killing Effect on Multiple Myeloma Cells Via Repressing SOCS1 Methylation-Mediated JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the effect of tetra-arsenic tetra-sulfide on treating multiple myeloma and its potential regulation on suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 methylation-mediated Janus kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway.
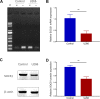
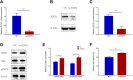
Methods: Tetra-arsenic tetra-sulfide with different concentrations were used to treat U266 cells, and cell viability was measured at 12, 24, and 48 hours with 0 μM tetra-arsenic tetra-sulfide treatment as control by Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 methylation and expression were determined by methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction, quantitative polymerase chain reaction, and Western blot, respectively, in U266 cells and normal plasma cells and in U266 cells treated by tetra-arsenic tetra-sulfide. Then, rescue experiments were performed by transfecting suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 small interfering RNA into tetra-arsenic tetra-sulfide-treated U266 cells. Besides, phosphor-Janus kinase 2, Janus kinase 2, phospho-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 expressions were determined by Western blot.
Results: Tetra-arsenic tetra-sulfide inhibited U266 cell viability efficiently in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 methylation was higher while suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 expression was lower in U266 cells compared to normal plasma cells; when treated by tetra-arsenic tetra-sulfide, suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 methylation was decreased while suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 expression was increased in U266 cells, along with the reduced phospho-Janus kinase 2 and phospho-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 expressions. Then, suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 small interfering RNA enhanced the cell viability and phospho-Janus kinase 2 as well as phospho-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 expressions in both tetra-arsenic tetra-sulfide treatment-free and tetra-arsenic tetra-sulfide-treated U266 cells.
Conclusion: Tetra-arsenic tetra-sulfide exhibits good killing effect on multiple myeloma cells via repressing suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 methylation and downstream Janus kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway, which might serve as a potential treatment option for multiple myeloma.
Keywords: As4S4; JAK2/STAT3; SOCS1 methylation; cell viability; multiple myeloma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Janus activated kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathway mediates icariside II-induced apoptosis in U266 multiple myeloma cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Mar 1;654(1):10-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.11.032. Epub 2010 Dec 21. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21172343
-
Inhibition of JAK1/STAT3 signaling mediates compound K-induced apoptosis in human multiple myeloma U266 cells.Food Chem Toxicol. 2011 Jun;49(6):1367-72. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2011.03.021. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Food Chem Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21420464
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathway mediates genipin-induced apoptosis in U266 multiple myeloma cells.J Cell Biochem. 2011 Jun;112(6):1552-62. doi: 10.1002/jcb.23077. J Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21344490
-
[Research Progress on Effect of Bone Marrow Microenvironment Regulated by IL-6/IL-6R/JAK2/STAT3 Pathway on Biological Behavior of Multiple Myeloma--Review].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Feb;32(1):318-321. doi: 10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2024.01.052. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38387942 Review. Chinese.
-
Biological Hallmarks and Emerging Strategies to Target STAT3 Signaling in Multiple Myeloma.Cells. 2022 Mar 10;11(6):941. doi: 10.3390/cells11060941. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35326392 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory Effect of JAK2/STAT3 on the Immune Function of Endotoxin-tolerant Dendritic Cells and its Involvement in Acute Liver Failure.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2022 Oct 28;10(5):879-890. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2021.00175. Epub 2022 Jan 4. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 36304491 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-17 activates JAK2/STAT3, PI3K/Akt and nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway to promote the tumorigenesis of cervical cancer.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Nov;22(5):1291. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10726. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34630646 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic ablation for liver malignancies: initial experience at a Scandinavian high volume HPB center.Surg Endosc. 2024 Oct;38(10):5785-5792. doi: 10.1007/s00464-024-11125-x. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Surg Endosc. 2024. PMID: 39145873 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence in fracture detection on radiographs: a literature review.Jpn J Radiol. 2025 Apr;43(4):551-585. doi: 10.1007/s11604-024-01702-4. Epub 2024 Nov 14. Jpn J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39538068 Review.
References
-
- Jin Z, Zhou S, Zhang Y, et al. Lycorine induces cell death in MM by suppressing Janus Kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription via inducing the expression of SOCS1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;84:1645–1653. - PubMed
-
- Wang M, Liu S, Liu P. Gene expression profile of multiple myeloma cell line treated by arsenic trioxide. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2007;27(6):646–649. - PubMed
-
- Moreau P, Attal M, Facon T. Frontline therapy of multiple myeloma. Blood. 2015;125(20):3076–3084. - PubMed
-
- Rollig C, Knop S, Bornhauser M. Multiple myeloma. Lancet. 2015;385(9983):2197–2208. - PubMed
-
- Hu J, Hu WX. Targeting signaling pathways in multiple myeloma: pathogenesis and implication for treatments. Cancer Lett. 2018;414:214–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

