Acute cerebellar knockdown of Sgce reproduces salient features of myoclonus-dystonia (DYT11) in mice
- PMID: 31868164
- PMCID: PMC6959989
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.52101
Acute cerebellar knockdown of Sgce reproduces salient features of myoclonus-dystonia (DYT11) in mice
Abstract
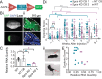
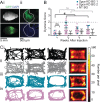
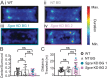
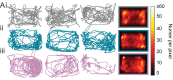
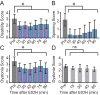
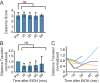
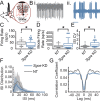
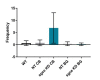
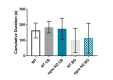
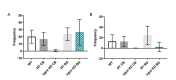
Myoclonus dystonia (DYT11) is a movement disorder caused by loss-of-function mutations in SGCE and characterized by involuntary jerking and dystonia that frequently improve after drinking alcohol. Existing transgenic mouse models of DYT11 exhibit only mild motor symptoms, possibly due to rodent-specific developmental compensation mechanisms, which have limited the study of neural mechanisms underlying DYT11. To circumvent potential compensation, we used short hairpin RNA (shRNA) to acutely knock down Sgce in the adult mouse and found that this approach produced dystonia and repetitive, myoclonic-like, jerking movements in mice that improved after administration of ethanol. Acute knockdown of Sgce in the cerebellum, but not the basal ganglia, produced motor symptoms, likely due to aberrant cerebellar activity. The acute knockdown model described here reproduces the salient features of DYT11 and provides a platform to study the mechanisms underlying symptoms of the disorder, and to explore potential therapeutic options.
Keywords: DYT11; alcohol responsive dystonia; mouse; myoclonus dystonia; neuroscience.
© 2019, Washburn et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SW, RF, MM, CA, KK No competing interests declared
Figures


References
-
- Asmus F, Zimprich A, Tezenas Du Montcel S, Kabus C, Deuschl G, Kupsch A, Ziemann U, Castro M, Kühn AA, Strom TM, Vidailhet M, Bhatia KP, Dürr A, Wood NW, Brice A, Gasser T. Myoclonus-dystonia syndrome: epsilon-sarcoglycan mutations and phenotype. Annals of Neurology. 2002;52:489–492. doi: 10.1002/ana.10325. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Azoulay-Zyss J, Roze E, Welter ML, Navarro S, Yelnik J, Clot F, Bardinet E, Karachi C, Dormont D, Galanaud D, Pidoux B, Cornu P, Vidailhet M, Grabli D. Bilateral deep brain stimulation of the pallidum for myoclonus-dystonia due to ε-sarcoglycan mutations: a pilot study. Archives of Neurology. 2011;68:94–98. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2010.338. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Beukers RJ, Foncke EM, van der Meer JN, Nederveen AJ, de Ruiter MB, Bour LJ, Veltman DJ, Tijssen MA. Disorganized sensorimotor integration in mutation-positive myoclonus-dystonia: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Archives of Neurology. 2010;67:469–474. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2010.54. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

