Metabolic modulation regulates cardiac wall morphogenesis in zebrafish
- PMID: 31868165
- PMCID: PMC7000217
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.50161
Metabolic modulation regulates cardiac wall morphogenesis in zebrafish
Abstract
During cardiac development, cardiomyocytes form complex inner wall structures called trabeculae. Despite significant investigation into this process, the potential role of metabolism has not been addressed. Using single cell resolution imaging in zebrafish, we find that cardiomyocytes seeding the trabecular layer actively change their shape while compact layer cardiomyocytes remain static. We show that Erbb2 signaling, which is required for trabeculation, activates glycolysis to support changes in cardiomyocyte shape and behavior. Pharmacological inhibition of glycolysis impairs cardiac trabeculation, and cardiomyocyte-specific loss- and gain-of-function manipulations of glycolysis decrease and increase trabeculation, respectively. In addition, loss of the glycolytic enzyme pyruvate kinase M2 impairs trabeculation. Experiments with rat neonatal cardiomyocytes in culture further support these observations. Our findings reveal new roles for glycolysis in regulating cardiomyocyte behavior during cardiac wall morphogenesis.
Keywords: cardiomyocytes; cell biology; developmental biology; glycolysis; heart development; metabolism; trabeculation; zebrafish.
© 2019, Fukuda et al.
Conflict of interest statement
RF, AA, YO, OS, ME, HM, MP, ET No competing interests declared, DS Senior editor, eLife
Figures
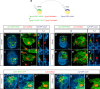
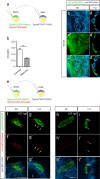
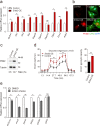




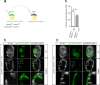

Comment in
-
Metabolism makes and mends the heart.Elife. 2020 Feb 4;9:e54665. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54665. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32014108 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carpenter RL, Paw I, Dewhirst MW, Lo H-W. Akt phosphorylates and activates HSF-1 independent of heat shock, leading to Slug overexpression and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2015;34:546–557. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.582. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

