Short-course quinazoline drug treatments are effective in the Litomosoides sigmodontis and Brugia pahangi jird models
- PMID: 31869759
- PMCID: PMC6931063
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2019.12.001
Short-course quinazoline drug treatments are effective in the Litomosoides sigmodontis and Brugia pahangi jird models
Abstract
The quinazolines CBR417 and CBR490 were previously shown to be potent anti-wolbachials that deplete Wolbachia endosymbionts of filarial nematodes and present promising pre-clinical candidates for human filarial diseases such as onchocerciasis. In the present study we tested both candidates in two models of chronic filarial infection, namely the Litomosoides sigmodontis and Brugia pahangi jird model and assessed their long-term effect on Wolbachia depletion, microfilariae counts and filarial embryogenesis 16-18 weeks after treatment initiation (wpt). Once per day (QD) oral treatment with CBR417 (50 mg/kg) for 4 days or twice per day (BID) with CBR490 (25 mg/kg) for 7 days during patent L. sigmodontis infection reduced the Wolbachia load by >99% and completely cleared peripheral microfilaremia from 10-14 wpt. Similarly, 7 days of QD treatments (40 mg/kg) with CBR417 or CBR490 cleared >99% of Wolbachia from B. pahangi and reduced peritoneal microfilariae counts by 93% in the case of CBR417 treatment. Transmission electron microscopy analysis indicated intensive damage to the B. pahangi ovaries following CBR417 treatment and in accordance filarial embryogenesis was inhibited in both models after CBR417 or CBR490 treatment. Suboptimal treatment regimens of CBR417 or CBR490 did not lead to a maintained reduction of the microfilariae and Wolbachia load. In conclusion, CBR417 or CBR490 are pre-clinical candidates for filarial diseases, which achieve long-term clearance of Wolbachia endosymbionts of filarial nematodes, inhibit filarial embryogenesis and clear microfilaremia with treatments as short as 7 days.
Keywords: Brugia pahangi; Doxycycline; Filaria; Litomosoides sigmodontis; Macrofilaricidal; Microfilariae; Quinazoline; Wolbachia.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures




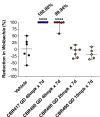
 ) or treated bi-daily (BID) with 40 mg/kg doxycycline for 14 days (
) or treated bi-daily (BID) with 40 mg/kg doxycycline for 14 days ( ), once per day (QD) with 50 mg/kg CBR417 for 4 days (
), once per day (QD) with 50 mg/kg CBR417 for 4 days ( ) or BID with 75 (
) or BID with 75 ( ) or 25 mg/kg (
) or 25 mg/kg ( ) CBR490 for 7 days. B: 16-week-infected jirds were either treated BID with vehicle control for 7 days (
) CBR490 for 7 days. B: 16-week-infected jirds were either treated BID with vehicle control for 7 days ( ), BID with 40 mg/kg doxycycline for 14 days (
), BID with 40 mg/kg doxycycline for 14 days ( ), QD with 50 (
), QD with 50 ( ), 20 (
), 20 ( ) or 10 (
) or 10 ( ) mg/kg CBR417 for 7 days, QD with 20 (
) mg/kg CBR417 for 7 days, QD with 20 ( ) or 10 (
) or 10 ( ) mg/kg CBR490 for 7 days or BID with 25 mg/kg CBR490 for 7 days (
) mg/kg CBR490 for 7 days or BID with 25 mg/kg CBR490 for 7 days ( ). Jirds were sacrificed 16 (A) or 18 (B) weeks after treatment. N = 5–6 per group.
). Jirds were sacrificed 16 (A) or 18 (B) weeks after treatment. N = 5–6 per group.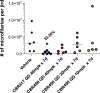



Similar articles
-
Corallopyronin A for short-course anti-wolbachial, macrofilaricidal treatment of filarial infections.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Dec 7;14(12):e0008930. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008930. eCollection 2020 Dec. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 33284808 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of short-course antiwolbachial quinazolines for elimination of filarial worm infections.Sci Transl Med. 2019 May 8;11(491):eaav3523. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav3523. Sci Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31068442
-
In vivo efficacy of the boron-pleuromutilin AN11251 against Wolbachia of the rodent filarial nematode Litomosoides sigmodontis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Jan 27;14(1):e0007957. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007957. eCollection 2020 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 31986143 Free PMC article.
-
Wolbachia in filarial nematodes: evolutionary aspects and implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of filarial diseases.Vet Parasitol. 2001 Jul 12;98(1-3):215-38. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4017(01)00432-0. Vet Parasitol. 2001. PMID: 11516587 Review.
-
A new approach to the treatment of filariasis.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2001 Dec;14(6):727-31. doi: 10.1097/00001432-200112000-00011. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2001. PMID: 11964892 Review.
Cited by
-
The Eagle effect in the Wolbachia-worm symbiosis.Parasit Vectors. 2021 Feb 24;14(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04545-w. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 33627171 Free PMC article.
-
Oxfendazole mediates macrofilaricidal efficacy against the filarial nematode Litomosoides sigmodontis in vivo and inhibits Onchocerca spec. motility in vitro.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Jul 6;14(7):e0008427. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008427. eCollection 2020 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32628671 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of the Management of Mansonellosis.Res Rep Trop Med. 2021 May 24;12:93-105. doi: 10.2147/RRTM.S274684. eCollection 2021. Res Rep Trop Med. 2021. PMID: 34079424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corallopyronin A for short-course anti-wolbachial, macrofilaricidal treatment of filarial infections.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Dec 7;14(12):e0008930. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008930. eCollection 2020 Dec. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 33284808 Free PMC article.
-
Combinations of the azaquinazoline anti-Wolbachia agent, AWZ1066S, with benzimidazole anthelmintics synergise to mediate sub-seven-day sterilising and curative efficacies in experimental models of filariasis.Front Microbiol. 2024 Feb 1;15:1346068. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1346068. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38362501 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bakowski M.A., Shiroodi R.K., Liu R., Olejniczak J., Yang B., Gagaring K., Guo H., White P.M., Chappell L., Debec A., Landmann F., Dubben B., Lenz F., Struever D., Ehrens A., Frohberger S.J., Sjoberg H., Pionnier N., Murphy E., Archer J., Steven A., Chunda V.C., Fombad F.F., Chounna P.W., Njouendou A.J., Metuge H.M., Ndzeshang B.L., Gandjui N.V., Akumtoh D.N., Kwenti T.D.B., Woods A.K., Joseph S.B., Hull M.V., Xiong W., Kuhen K.L., Taylor M.J., Wanji S., Turner J.D., Hubner M.P., Hoerauf A., Chatterjee A.K., Roland J., Tremblay M.S., Schultz P.G., Sullivan W., Chu X.J., Petrassi H.M., McNamara C.W. Discovery of short-course antiwolbachial quinazolines for elimination of filarial worm infections. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019;11(491) - PubMed
-
- Debrah A.Y., Specht S., Klarmann-Schulz U., Batsa L., Mand S., Marfo-Debrekyei Y., Fimmers R., Dubben B., Kwarteng A., Osei-Atweneboana M., Boakye D., Ricchiuto A., Buttner M., Adjei O., Mackenzie C.D., Hoerauf A. Doxycycline leads to sterility and enhanced killing of female Onchocerca volvulus worms in an area with persistent microfilaridermia after repeated ivermectin treatment: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015;61:517–526. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Desjardins C.A., Cerqueira G.C., Goldberg J.M., Hotopp J.C., Haas B.J., Zucker J., Ribeiro J.M., Saif S., Levin J.Z., Fan L., Zeng Q., Russ C., Wortman J.R., Fink D.L., Birren B.W., Nutman T.B. Genomics of Loa loa, a Wolbachia-free filarial parasite of humans. Nat. Genet. 2013;45:495–500. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

