Bupropion Inhibits Serotonin Type 3AB Heteromeric Channels at Clinically Relevant Concentrations
- PMID: 31871303
- PMCID: PMC6978693
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.119.118349
Bupropion Inhibits Serotonin Type 3AB Heteromeric Channels at Clinically Relevant Concentrations
Abstract
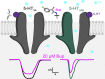
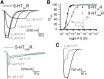
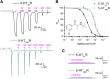
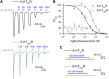
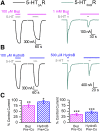
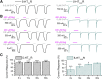
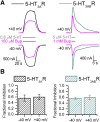
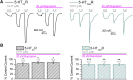
Bupropion, a Food and Drug Administration-approved antidepressant and smoking cessation aid, blocks dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake transporters and noncompetitively inhibits nicotinic acetylcholine and serotonin (5-HT) type 3A receptors (5-HT3ARs). 5-HT3 receptors are pentameric ligand-gated ion channels that regulate synaptic activity in the central and peripheral nervous system, presynaptically and postsynaptically. In the present study, we examined and compared the effect of bupropion and its active metabolite hydroxybupropion on mouse homomeric 5-HT3A and heteromeric 5-HT3AB receptors expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes using two-electrode voltage clamp experiments. Coapplication of bupropion or hydroxybupropion with 5-HT dose dependently inhibited 5-HT-induced currents in heteromeric 5-HT type 3AB receptors (5-HT3ABRs) (IC50 = 840 and 526 μM, respectively). The corresponding IC50s for bupropion and hydroxybupropion for homomeric 5-HT3ARs were 10- and 5-fold lower, respectively (87 and 113 μM). The inhibition of 5-HT3ARs and 5-HT3ABRs was non-use dependent and voltage independent, suggesting bupropion is not an open channel blocker. The inhibition by bupropion was reversible and time-dependent. Of note, preincubation with a low concentration of bupropion that mimics therapeutic drug conditions inhibits 5-HT-induced currents in 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors considerably. In summary, we demonstrate that bupropion inhibits heteromeric 5-HT3ABRs as well as homomeric 5-HT3ARs. This inhibition occurs at clinically relevant concentrations and may contribute to bupropion's clinical effects. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Clinical studies indicate that antagonizing serotonin (5-HT) type 3AB (5-HT3AB) receptors in brain areas involved in mood regulation is successful in treating mood and anxiety disorders. Previously, bupropion was shown to be an antagonist at homopentameric 5-HT type 3A receptors. The present work provides novel insights into the pharmacological effects that bupropion exerts on heteromeric 5-HT3AB receptors, in particular when constantly present at low, clinically attainable concentrations. The results advance the knowledge on the clinical effects of bupropion as an antidepressant.
Copyright © 2020 by The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
The antidepressant bupropion is a negative allosteric modulator of serotonin type 3A receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Feb;113(Pt A):89-99. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.09.021. Epub 2016 Sep 24. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 27671323 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer drug irinotecan inhibits homomeric 5-HT3A and heteromeric 5-HT3AB receptor responses.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Nov 18;415(2):416-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.10.084. Epub 2011 Oct 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 22044840
-
General anesthetic-induced channel gating enhancement of 5-hydroxytryptamine type 3 receptors depends on receptor subunit composition.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Nov;315(2):771-6. doi: 10.1124/jpet.105.090621. Epub 2005 Aug 4. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005. PMID: 16081679
-
Bupropion: a review of its mechanism of antidepressant activity.J Clin Psychiatry. 1995 Sep;56(9):395-401. J Clin Psychiatry. 1995. PMID: 7665537 Review.
-
Therapeutics of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists: current uses and future directions.Pharmacol Ther. 2011 Jun;130(3):338-47. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2011.02.003. Epub 2011 Feb 26. Pharmacol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21356241 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of a binding site for bupropion in Gloeobacter violaceus ligand-gated ion channel.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 10:2023.10.09.561596. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.09.561596. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Biophys J. 2024 Jul 16;123(14):2185-2198. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.04.027. PMID: 37873398 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Revisiting bupropion anti-inflammatory action: involvement of the TLR2/TLR4 and JAK2/STAT3.Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Aug;29(4):1101-1109. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00829-4. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Inflammopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34218389
-
A bupropion modulatory site in the Gloeobacter violaceus ligand-gated ion channel.Biophys J. 2024 Jul 16;123(14):2185-2198. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.04.027. Epub 2024 Apr 27. Biophys J. 2024. PMID: 38678367 Free PMC article.
-
Mobility of Lower MA-Helices for Ion Conduction through Lateral Portals in 5-HT3A Receptors.Biophys J. 2020 Dec 15;119(12):2593-2603. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.10.029. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 33157122 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Nicergoline from Ergot Fungus in Blocking Human 5-HT3A Receptor.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Nov 29;35:e2411020. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2411.11020. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39849925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkondon M, Albuquerque EX. (2005) Nicotinic receptor subtypes in rat hippocampal slices are differentially sensitive to desensitization and early in vivo functional up-regulation by nicotine and to block by bupropion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 313:740–750. - PubMed
-
- Arias HR. (2009) Is the inhibition of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors by bupropion involved in its clinical actions? Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:2098–2108. - PubMed
-
- Aznar S, Kostova V, Christiansen SH, Knudsen GM. (2005) Alpha 7 nicotinic receptor subunit is present on serotonin neurons projecting to hippocampus and septum. Synapse 55:196–200. - PubMed
-
- Bétry C, Etiévant A, Oosterhof C, Ebert B, Sanchez C, Haddjeri N. (2011) Role of 5-HT(3) receptors in the antidepressant response. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 4:603–629.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

