Targeting alpha synuclein and amyloid beta by a multifunctional, brain-penetrant dopamine D2/D3 agonist D-520: Potential therapeutic application in Parkinson's disease with dementia
- PMID: 31873106
- PMCID: PMC6927976
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-55830-3
Targeting alpha synuclein and amyloid beta by a multifunctional, brain-penetrant dopamine D2/D3 agonist D-520: Potential therapeutic application in Parkinson's disease with dementia
Abstract
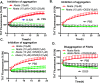
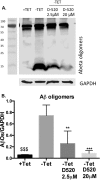
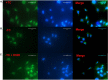
A significant number of people with Parkinson's disease (PD) develop dementia in addition to cognitive dysfunction and are diagnosed as PD with dementia (PDD). This is characterized by cortical and limbic alpha synuclein (α-syn) accumulation, and high levels of diffuse amyloid beta (Aβ) plaques in the striatum and neocortical areas. In this regard, we evaluated the effect of a brain-penetrant, novel multifunctional dopamine D2/D3 agonist, D-520 on the inhibition of Aβ aggregation and disintegration of α-syn and Aβ aggregates in vitro using purified proteins and in a cell culture model that produces intracellular Aβ-induced toxicity. We further evaluated the effect of D-520 in a Drosophila model of Aβ1-42 toxicity. We report that D-520 inhibits the formation of Aβ aggregates in vitro and promotes the disaggregation of both α-syn and Aβ aggregates. Finally, in an in vivo Drosophila model of Aβ1-42 dependent toxicity, D-520 exhibited efficacy by rescuing fly eyes from retinal degeneration caused by Aβ toxicity. Our data indicate the potential therapeutic applicability of D-520 in addressing motor dysfunction and neuroprotection in PD and PDD, as well as attenuating dementia in people with PDD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Novel multifunctional dopamine D2/D3 receptors agonists with potential neuroprotection and anti-alpha synuclein protein aggregation properties.Bioorg Med Chem. 2016 Nov 1;24(21):5088-5102. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.08.021. Epub 2016 Aug 20. Bioorg Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27591013
-
The Role of NOX4 in Parkinson's Disease with Dementia.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 6;20(3):696. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030696. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30736297 Free PMC article.
-
A novel iron (II) preferring dopamine agonist chelator D-607 significantly suppresses α-syn- and MPTP-induced toxicities in vivo.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Sep 1;123:88-99. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.05.019. Epub 2017 May 19. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28533164 Free PMC article.
-
From the cell to the clinic: a comparative review of the partial D₂/D₃receptor agonist and α2-adrenoceptor antagonist, piribedil, in the treatment of Parkinson's disease.Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Nov;128(2):229-73. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.06.002. Epub 2010 Jun 26. Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20600305 Review.
-
Parkinson's disease dementia: convergence of α-synuclein, tau and amyloid-β pathologies.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013 Sep;14(9):626-36. doi: 10.1038/nrn3549. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23900411 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
On the Chemical and Biological Characteristics of Multifunctional Compounds for the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jan 17;12(2):214. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020214. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Microglial α-Synuclein/TLRs/NF-kappaB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Axis in Parkinson's Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 8;12:719807. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.719807. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34691027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Aggregation in the Pathogenesis of Ischemic Stroke.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Aug;41(6):1183-1194. doi: 10.1007/s10571-020-00899-y. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 32529541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traumatic brain injury and the development of parkinsonism: Understanding pathophysiology, animal models, and therapeutic targets.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 May;149:112812. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112812. Epub 2022 Mar 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35290887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding crosstalk between neurotransmitters and α-synuclein in Parkinson's disease: pathogenesis and therapeutic implications.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2025 Jun 5;18:17562864251339895. doi: 10.1177/17562864251339895. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2025. PMID: 40486190 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
