Spinal subpial delivery of AAV9 enables widespread gene silencing and blocks motoneuron degeneration in ALS
- PMID: 31873312
- PMCID: PMC8171115
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-019-0674-1
Spinal subpial delivery of AAV9 enables widespread gene silencing and blocks motoneuron degeneration in ALS
Abstract
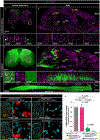
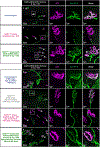
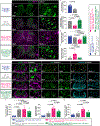
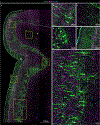
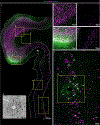
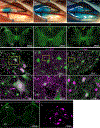
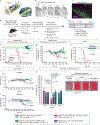
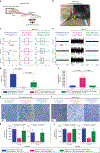
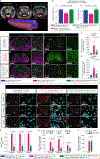
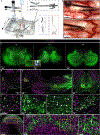
Gene silencing with virally delivered shRNA represents a promising approach for treatment of inherited neurodegenerative disorders. In the present study we develop a subpial technique, which we show in adult animals successfully delivers adeno-associated virus (AAV) throughout the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spinal cord, as well as brain motor centers. One-time injection at cervical and lumbar levels just before disease onset in mice expressing a familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)-causing mutant SOD1 produces long-term suppression of motoneuron disease, including near-complete preservation of spinal α-motoneurons and muscle innervation. Treatment after disease onset potently blocks progression of disease and further α-motoneuron degeneration. A single subpial AAV9 injection in adult pigs or non-human primates using a newly designed device produces homogeneous delivery throughout the cervical spinal cord white and gray matter and brain motor centers. Thus, spinal subpial delivery in adult animals is highly effective for AAV-mediated gene delivery throughout the spinal cord and supraspinal motor centers.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
M. Marsala is the scientific founder of Neurgain Technologies, Inc. and has an equity interest in the company. In addition, he serves as a consultant to Neurgain Technologies, Inc., and receives compensation for these services. The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by the University of California San Diego in accordance with its policies on conflict of interests. B.K.K. is a Chief Scientific Officer in Avexis Inc. All other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures






References
-
- Rosen DR et al. Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 362, 59–62 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto A et al. Disease progression of human SOD1 (G93A) transgenic ALS model rats. J. Neurosci. Res. 83, 119–133 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Kaur SJ, McKeown SR & Rashid S Mutant SOD1 mediated pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Gene 577, 109–118 (2016). - PubMed
-
- van Zundert B & Brown RH Jr. Silencing strategies for therapy of SOD1-mediated ALS. Neurosci. Lett. 636, 32–39 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

