Analysis of multidrug resistance in Streptococcus suis ATCC 700794 under tylosin stress
- PMID: 31874073
- PMCID: PMC6363075
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2018.1557505
Analysis of multidrug resistance in Streptococcus suis ATCC 700794 under tylosin stress
Abstract
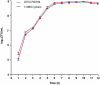
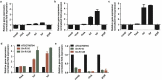
Streptococcus suis is an important zoonotic pathogen. The massive use of tylosin and other antibiotics in swine production has led to the emergence of resistant phenotypes of S. suis. However, there are no adequate measures available to address the problem of bacterial resistance. This study involved the use of 1/4 MIC (0.125 µg/mL) of tylosin to investigate resistance-related proteins by S. suis ATCC 700794. Our results showed that 171 proteins were differentially expressed in S. suis tested with 1/4 MIC (0.125 µg/mL) of tylosin using iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic methods. TCS, heat shock protein and elongation factors were differentially expressed at 1/4 MIC (0.125 µg/mL) of tylosin compared to non treated, control cells. Using quantitative RT-PCR analysis, we verified the relationship between the differentially expressed proteins in S. suis with different MIC values. The data showed that expression profile for elongation factor G (fusA), elongation factor Ts (tsf), elongation factor Tu (tuf), putative histidine kinase of the competence regulon, ComD (comD), putative competence-damage inducible protein (cinA) and protein GrpE (grpE), observed in tylosin-resistant S. suis, correlated with that of S. suis ATCC 700794 at 1/4 MIC (0.125 µg/mL). The MIC of tylosin-resistant showed high-level resistance in terramycin, chlortetracycline, ofloxacin and enrofloxacin. Our findings demonstrated the importance of elongation factors, TCS and heat shock protein during development of tylosin resistance in S. suis. Thus, our study will provide insight into new drug targets and help reduce bacterial multidrug resistance through development of corresponding inhibitors.
Keywords: Streptococcus suis; iTRAQ; multidrug resistance; tylosin.
Figures


References
-
- Sugawara A, Maruyama H, Shibusawa S, et al. 5-O-Mycaminosyltylonolide antibacterial derivatives: design, synthesis and bioactivity [Article]. J Antibiot. 2017. August;70(8):878–887. PubMed PMID: WOS:000406255800003; English. - PubMed
-
- Gottschalk M, Xu JG, Calzas C, et al. Streptococcus suis: a new emerging or an old neglected zoonotic pathogen? [Article]. Future Microbiol. 2010. March;5(3):371–391. PubMed PMID: WOS:000276191300011; English. - PubMed
-
- Aarestrup FM, Carstensen B.. Effect of tylosin used as a growth promoter on the occurrence of macrolide-resistant enterococci and staphylococci in pigs [; Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t]. Microbial Drug Resist (Larchmont, NY). 1998;4(4):307–312. PubMed PMID: MEDLINE:9988049; English. - PubMed
-
- de Jong A, Simjee S, El Garch F, et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility of enterococci recovered from healthy cattle, pigs and chickens in nine EU countries (EASSA Study) to critically important antibiotics [Article]. Vet Microbiol. 2018. March;216:168–175. PubMed PMID: WOS:000428487800024; English. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
