Development of structure-function coupling in human brain networks during youth
- PMID: 31874926
- PMCID: PMC6955327
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1912034117
Development of structure-function coupling in human brain networks during youth
Abstract
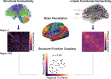
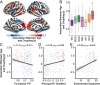
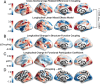
The protracted development of structural and functional brain connectivity within distributed association networks coincides with improvements in higher-order cognitive processes such as executive function. However, it remains unclear how white-matter architecture develops during youth to directly support coordinated neural activity. Here, we characterize the development of structure-function coupling using diffusion-weighted imaging and n-back functional MRI data in a sample of 727 individuals (ages 8 to 23 y). We found that spatial variability in structure-function coupling aligned with cortical hierarchies of functional specialization and evolutionary expansion. Furthermore, hierarchy-dependent age effects on structure-function coupling localized to transmodal cortex in both cross-sectional data and a subset of participants with longitudinal data (n = 294). Moreover, structure-function coupling in rostrolateral prefrontal cortex was associated with executive performance and partially mediated age-related improvements in executive function. Together, these findings delineate a critical dimension of adolescent brain development, whereby the coupling between structural and functional connectivity remodels to support functional specialization and cognition.
Keywords: MRI; brain development; connectome; cortical organization; structure–function.
Copyright © 2020 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Huntenburg J. M., Bazin P.-L., Margulies D. S., Large-scale gradients in human cortical organization. Trends Cogn. Sci. 22, 21–31 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 NS085211/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH107235/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K08 MH120564/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH113550/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F31 MH115709/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH102609/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD023495/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- T32 EB009653/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 MH116920/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH096891/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH112847/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH119219/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH107703/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

