Bacterial microbiota composition of Ixodes ricinus ticks: the role of environmental variation, tick characteristics and microbial interactions
- PMID: 31875152
- PMCID: PMC6925955
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.8217
Bacterial microbiota composition of Ixodes ricinus ticks: the role of environmental variation, tick characteristics and microbial interactions
Abstract
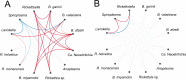
Ecological factors, host characteristics and/or interactions among microbes may all shape the occurrence of microbes and the structure of microbial communities within organisms. In the past, disentangling these factors and determining their relative importance in shaping within-host microbiota communities has been hampered by analytical limitations to account for (dis)similar environmental preferences ('environmental filtering'). Here we used a joint species distribution modelling (JSDM) approach to characterize the bacterial microbiota of one of the most important disease vectors in Europe, the sheep tick Ixodes ricinus, along ecological gradients in the Swiss Alps. Although our study captured extensive environmental variation along elevational clines, the explanatory power of such large-scale ecological factors was comparably weak, suggesting that tick-specific traits and behaviours, microhabitat and -climate experienced by ticks, and interactions among microbes play an important role in shaping tick microbial communities. Indeed, when accounting for shared environmental preferences, evidence for significant patterns of positive or negative co-occurrence among microbes was found, which is indicative of competition or facilitation processes. Signals of facilitation were observed primarily among human pathogens, leading to co-infection within ticks, whereas signals of competition were observed between the tick endosymbiont Spiroplasma and human pathogens. These findings highlight the important role of small-scale ecological variation and microbe-microbe interactions in shaping tick microbial communities and the dynamics of tick-borne disease.
Keywords: Borrelia burgdorferi; Community composition; Lyme disease; Species distribution modelling; Tick-borne pathogens.
©2019 Aivelo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Abraham NM, Liu L, Jutras BL, Yadav AK, Narasimhan S, Gopalakrishnan V, Ansari JM, Jefferson KK, Cava F, Jacobs-Wagner C, Fikrig E. Pathogen-mediated manipulation of arthropod microbiota to promote infection. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2017;114:E781–E790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1613422114. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abrego N, Norberg A, Ovaskainen O. Measuring and predicting the influence of traits on the assembly processes of wood-inhabiting fungi. Journal of Ecology. 2016;105:1070–1081. doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.12722. - DOI
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

