The Preparedness of Hospital Emergency Departments for Responding to Disasters in Iran; a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 31875212
- PMCID: PMC6905417
The Preparedness of Hospital Emergency Departments for Responding to Disasters in Iran; a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Hospitals are the most important infrastructures of any society. The hospital emergency department is one of the most important wards of hospitals in response to disasters. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the preparedness of hospital emergency departments in response to disasters in Iran via a systematic review and meta-analysis.
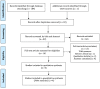
Methods: This study was a systematic review and meta-analysis. The literature search was conducted in the national and international databases including SID, Magiran, Irandoc, Google scholar, Medline, Scopus, and ISI. Valid Persian and English keywords were used to extract articles related to the preparedness of hospital emergency departments in response to disasters. The STROBE checklist was used to evaluate the quality of the articles, and the I2 index was used to assess heterogeneity among the studies. Statistical analyses were conducted using STATA14 software.
Results: In this study, 185 articles were initially recruited. Meta-analysis was finally performed on 4 articles selected based on inclusion criteria. The analysis included a total of 51 hospitals in Iran. According to our results, the mean preparedness of hospital emergency departments in response to disasters was calculated as 54.64% (95% CI = 41.15-68.13, I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.727).
Conclusion: The results of this study showed that the average level of preparedness of hospital emergency departments in Iran to respond to disasters was moderate to high. Therefore, planning and actions should be considered based on the guidelines and accreditation standards to enhance the preparedness of hospital emergency departments in response to disasters.
Keywords: Disasters; disaster medicine; emergency service; hospital; meta-analysis as topic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Earthquake Preparedness in Iranian Hospitals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Bull Emerg Trauma. 2021 Jan;9(1):1-8. doi: 10.30476/BEAT.2021.86968. Bull Emerg Trauma. 2021. PMID: 33937419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hospital Disaster Preparedness in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Iran J Public Health. 2020 May;49(5):837-850. Iran J Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32953672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knowledge, Attitude and Performance Associated with Disaster Preparedness in Iranian Nurses: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Adv J Emerg Med. 2019 Jul 24;3(4):e42. doi: 10.22114/ajem.v0i0.204. eCollection 2019 Fall. Adv J Emerg Med. 2019. PMID: 31633097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hospital Preparedness Measures for Biological Hazards: A Systematic Review and Meta-Synthesis.Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2021 Dec;15(6):790-803. doi: 10.1017/dmp.2020.132. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2021. PMID: 32713417
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
Cited by
-
Dimensions of hospital resilience emphasized during the COVID-19 pandemic response: A systematic review.Health Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 19;7(8):e2300. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.2300. eCollection 2024 Aug. Health Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39166122 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Suicide Ideation and Attempt during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Prev Med. 2023 Jan 25;14:9. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.ijpvm_507_21. eCollection 2023. Int J Prev Med. 2023. PMID: 36942038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Prevalence of Suicidal Ideation after the Earthquake: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Iran J Public Health. 2020 Dec;49(12):2330-2338. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v49i12.4815. Iran J Public Health. 2020. PMID: 34178739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Earthquake Preparedness in Iranian Hospitals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Bull Emerg Trauma. 2021 Jan;9(1):1-8. doi: 10.30476/BEAT.2021.86968. Bull Emerg Trauma. 2021. PMID: 33937419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: Impact of deployment in disaster situations on the mental health of emergency responders.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Sep 30;15:1481901. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1481901. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39403321 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Jahangiri K, Izadkhah YO, Lari A. Hospital safety index (HSI) analysis in confronting disasters: A case study from Iran. International Journal of Health System and Disaster Management. 2014;2(1)
-
- Ghafouri RR, Hosseini SM, Pouraghaei M. Are our hospitals safe against disasters? An evaluation of hospital safety index in Tabriz, Iran. Journal of Analytical Research in Clinical Medicine. 2018;6(3):139–44.
-
- Nekoie-Moghadam M, Kurland L, Moosazadeh M, Ingrassia PL, Della Corte F, Djalali A. Tools and checklists used for the evaluation of hospital disaster preparedness: a systematic review. Disaster medicine and public health preparedness. 2016;10(5):781–8. - PubMed
-
- Asefzadeh S, Rajaee R, Ghamari F, Kalhor R, Gholami S. Preparedness of Iranian Hospitals Against Disasters. Biotechnology and Health Sciences. 2016;3(3):1–6.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources