TNFR2 Signaling Enhances ILC2 Survival, Function, and Induction of Airway Hyperreactivity
- PMID: 31875557
- PMCID: PMC6940205
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.11.102
TNFR2 Signaling Enhances ILC2 Survival, Function, and Induction of Airway Hyperreactivity
Abstract
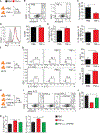
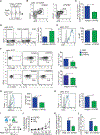
Group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) can initiate pathologic inflammation in allergic asthma by secreting copious amounts of type 2 cytokines, promoting lung eosinophilia and airway hyperreactivity (AHR), a cardinal feature of asthma. We discovered that the TNF/TNFR2 axis is a central immune checkpoint in murine and human ILC2s. ILC2s selectively express TNFR2, and blocking the TNF/TNFR2 axis inhibits survival and cytokine production and reduces ILC2-dependent AHR. The mechanism of action of TNFR2 in ILC2s is through the non-canonical NF-κB pathway as an NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) inhibitor blocks the costimulatory effect of TNF-α. Similarly, human ILC2s selectively express TNFR2, and using hILC2s, we show that TNFR2 engagement promotes AHR through a NIK-dependent pathway in alymphoid murine recipients. These findings highlight the role of the TNF/TNFR2 axis in pulmonary ILC2s, suggesting that targeting TNFR2 or relevant signaling is a different strategy for treating patients with ILC2-dependent asthma.
Keywords: ILC2; NIK; NIK inhibitor; TNF-a; TNFR2; activation; airway hyperreactivity; asthma.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
LAIR-1 acts as an immune checkpoint on activated ILC2s and regulates the induction of airway hyperreactivity.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022 Jan;149(1):223-236.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2021.05.042. Epub 2021 Jun 16. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34144112 Free PMC article.
-
SIRPα engagement regulates ILC2 effector function and alleviates airway hyperreactivity via modulating energy metabolism.Cell Mol Immunol. 2024 Oct;21(10):1158-1174. doi: 10.1038/s41423-024-01208-z. Epub 2024 Aug 19. Cell Mol Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39160226 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of type 2 innate lymphoid cell-dependent airway hyperreactivity by butyrate.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018 Dec;142(6):1867-1883.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.02.032. Epub 2018 Mar 6. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29522844
-
Non-canonical NF-κB signaling activation and regulation: principles and perspectives.Immunol Rev. 2011 Nov;244(1):44-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01059.x. Immunol Rev. 2011. PMID: 22017430 Review.
-
TNFR2: A Novel Target for Cancer Immunotherapy.Trends Mol Med. 2017 Nov;23(11):1037-1046. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2017.09.007. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Trends Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 29032004 Review.
Cited by
-
Fn14 and TNFR2 as regulators of cytotoxic TNFR1 signaling.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Nov 6;11:1267837. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1267837. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 38020877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate Lymphoid Cells Are Required to Induce Airway Hyperreactivity in a Murine Neutrophilic Asthma Model.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 15;13:849155. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.849155. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35371094 Free PMC article.
-
Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells: Protectors in Type 2 Diabetes.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 19;12:727008. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.727008. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34489979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic allergic asthma alters m6A epitranscriptomic tagging of mRNAs and lncRNAs in the lung.Biosci Rep. 2022 Dec 22;42(12):BSR20221395. doi: 10.1042/BSR20221395. Biosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36250525 Free PMC article.
-
Flow cytometric analysis of innate lymphoid cells: challenges and solutions.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 22;14:1198310. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1198310. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37809100 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aggarwal BB (2003). Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a doubleedged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol 3, 745–756. - PubMed
-
- Anticevich SZ, Hughes JM, Black JL, and Armour CL (1995). Induction of human airway hyperresponsiveness by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Eur. J. Pharmacol 284, 221–225. - PubMed
-
- Barlow JL, Peel S, Fox J, Panova V, Hardman CS, Camelo A, Bucks C, Wu X, Kane CM, Neill DR, et al. (2013). IL-33 is more potent than IL-25 in provoking IL-13-producing nuocytes (type 2 innate lymphoid cells) and airway contraction. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol 132, 933–941. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

