Expression and Function of Host Defense Peptides at Inflammation Sites
- PMID: 31877866
- PMCID: PMC6982121
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21010104
Expression and Function of Host Defense Peptides at Inflammation Sites
Abstract
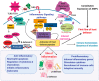
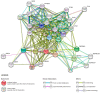
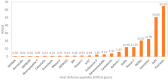
There is a growing interest in the complex role of host defense peptides (HDPs) in the pathophysiology of several immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. The physicochemical properties and selective interaction of HDPs with various receptors define their immunomodulatory effects. However, it is quite challenging to understand their function because some HDPs play opposing pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory roles, depending on their expression level within the site of inflammation. While it is known that HDPs maintain constitutive host protection against invading microorganisms, the inducible nature of HDPs in various cells and tissues is an important aspect of the molecular events of inflammation. This review outlines the biological functions and emerging roles of HDPs in different inflammatory conditions. We further discuss the current data on the clinical relevance of impaired HDPs expression in inflammation and selected diseases.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; cathelicidins; defensins; host defense peptides; human antimicrobial peptides; inflammation; pro-inflammatory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

