Vulpinic Acid Controls Stem Cell Fate toward Osteogenesis and Adipogenesis
- PMID: 31878002
- PMCID: PMC7017160
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11010018
Vulpinic Acid Controls Stem Cell Fate toward Osteogenesis and Adipogenesis
Abstract
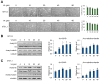
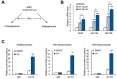
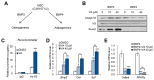
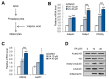
Vulpinic acid, a naturally occurring methyl ester of pulvinic acid, has been reported to exert anti-fungal, anti-cancer, and anti-oxidative effects. However, its metabolic action has not been implicated yet. Here, we show that vulpinic acid derived from a mushroom, Pulveroboletus ravenelii controls the cell fate of mesenchymal stem cells and preadipocytes by inducing the acetylation of histone H3 and α-tubulin, respectively. The treatment of 10T1/2 mesenchymal stem cells with vulpinic acid increased the expression of Wnt6, Wnt10a, and Wnt10b, which led to osteogenesis inhibiting the adipogenic lineage commitment, through the upregulation of H3 acetylation. By contrast, treatment with vulpinic acid promoted the terminal differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes into mature adipocytes. In this process, the increase in acetylated tubulin was accompanied, while acetylated H3 was not altered. As excessive generation of adipocytes occurs, the accumulation of lipid drops was not concentrated, but dispersed into a number of adipocytes. Consistently, the expressions of lipolytic genes were upregulated and inflammatory factors were downregulated in adipocytes exposed to vulpinic acid during adipogenesis. These findings reveal the multiple actions of vulpinic acid in two stages of differentiation, promoting the osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells and decreasing hypertrophic adipocytes, which can provide experimental evidence for the novel metabolic advantages of vulpinic acid.
Keywords: acetyl H3; acetyl tubulin; adipogenesis; cell fate; hypertrophy; osteogenesis; vulpinic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Baek S.C., Choi E., Eom H.J., Jo M.S., Kim S., So H.M., Kim S.H., Kang K.S., Kim K.H. LC/MS-based analysis of bioactive compounds from the bark of Betula platyphylla var. japonica and their effects on regulation of adipocyte and osteoblast differentiation. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2018;24:235–240. doi: 10.20307/nps.2018.24.4.235. - DOI
-
- Wei Y., Chen Y.H., Li L.Y., Lang J., Yeh S.P., Shi B., Yang C.C., Yang J.Y., Lin C.Y., Lai C.C., et al. CDK1-dependent phosphorylation of EZH2 suppresses methylation of H3K27 and promotes osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011;13:87–94. doi: 10.1038/ncb2139. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

