Biologically Active Echinulin-Related Indolediketopiperazines from the Marine Sediment-Derived Fungus Aspergillus niveoglaucus
- PMID: 31878044
- PMCID: PMC6983058
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25010061
Biologically Active Echinulin-Related Indolediketopiperazines from the Marine Sediment-Derived Fungus Aspergillus niveoglaucus
Abstract
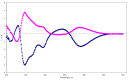
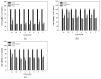
Seven known echinulin-related indolediketopiperazine alkaloids (1-7) were isolated from the Vietnamese sediment-derived fungus Aspergillus niveoglaucus. Using chiral HPLC, the enantiomers of cryptoechinuline B (1) were isolated as individual compounds for the first time. (+)-Cryptoechinuline B (1a) exhibited neuroprotective activity in 6-OHDA-, paraquat-, and rotenone-induced in vitro models of Parkinson's disease. (-)-Cryptoechinuline B (1b) and neoechinulin C (5) protected the neuronal cells against paraquat-induced damage in a Parkinson's disease model. Neoechinulin B (4) exhibited cytoprotective activity in a rotenone-induced model, and neoechinulin (7) showed activity in the 6-OHDA-induced model.
Keywords: 6-OHDA; Aspergillus niveoglaucus; NMR data; cryptoechinuline; cytotoxic activity; echinulin; neoechinulin; neuroprotective activity; paraquat; rotenone; urease inhibition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chen A.J., Hubka V., Frisvad J.C., Visagie C.M., Houbraken J., Meijer M., Varga J., Demirel R., Jurjević Z., Kubátová A., et al. Polyphasic taxonomy of Aspergillus section Aspergillus (formerly Eurotium), and its occurrence in indoor environments and food. Stud. Mycol. 2017;88:37–135. doi: 10.1016/j.simyco.2017.07.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

