Tackling Faults in the Industry 4.0 Era-A Survey of Machine-Learning Solutions and Key Aspects
- PMID: 31878065
- PMCID: PMC6983262
- DOI: 10.3390/s20010109
Tackling Faults in the Industry 4.0 Era-A Survey of Machine-Learning Solutions and Key Aspects
Abstract
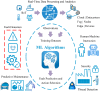
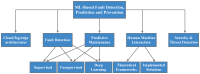
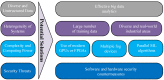
The recent advancements in the fields of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have affected several research fields, leading to improvements that could not have been possible with conventional optimization techniques. Among the sectors where AI/ML enables a plethora of opportunities, industrial manufacturing can expect significant gains from the increased process automation. At the same time, the introduction of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), providing improved wireless connectivity for real-time manufacturing data collection and processing, has resulted in the culmination of the fourth industrial revolution, also known as Industry 4.0. In this survey, we focus on the vital processes of fault detection, prediction and prevention in Industry 4.0 and present recent developments in ML-based solutions. We start by examining various proposed cloud/fog/edge architectures, highlighting their importance for acquiring manufacturing data in order to train the ML algorithms. In addition, as faults might also occur from sources beyond machine degradation, the potential of ML in safeguarding cyber-security is thoroughly discussed. Moreover, a major concern in the Industry 4.0 ecosystem is the role of human operators and workers. Towards this end, a detailed overview of ML-based human-machine interaction techniques is provided, allowing humans to be in-the-loop of the manufacturing processes in a symbiotic manner with minimal errors. Finally, open issues in these relevant fields are given, stimulating further research.
Keywords: Industry 4.0; anomaly detection; fault detection; human–machine interaction; machine learning; predictive maintenance; security.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chen B., Wan J., Shu L., Li P., Mukherjee M., Yin B. Smart Factory of Industry 4.0: Key Technologies, Application, and Challenges. IEEE Access. 2017;6:6505–6519. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2783682. - DOI
-
- Lu J. Industry 4.0: A Survey on Technologies, Applications and Open Research Issues. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2017;6:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jii.2017.04.005. - DOI
-
- Muhuri P.K., Shukla A.K., Abraham A. Industry 4.0: A Bibliometric Analysis and Detailed Overview. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2019;78:218–235. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2018.11.007. - DOI
-
- Xu L.D., Xu E.L., Li E. Industry 4.0: State of the Art and Future Trends. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018;56:2941–2962. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2018.1444806. - DOI
-
- Li B., Hou B., Yu W., Lu X., Yang C. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Intelligent Manufacturing: A Review. Front. Inf. Tech. Electron. Eng. 2017;18:89–96. doi: 10.1631/FITEE.1601885. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

