Treatment of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension in a multidisciplinary team
- PMID: 31878837
- PMCID: PMC6935880
- DOI: 10.1177/1753466619891529
Treatment of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension in a multidisciplinary team
Abstract
Background: Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) may be treated with pulmonary endarterectomy (PEA), balloon pulmonary angioplasty (BPA) and medical therapy (MT). Assessment in a multidisciplinary team of experts (CTEPH team) is currently recommended for treatment decision making. The aim of the present study was to report the effects of such an interdisciplinary concept.
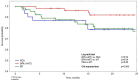
Methods and results: A total of 160 patients were consulted by the CTEPH team between December 2015 and September 2018. Patient baseline characteristics, CTEPH team decisions and implementation rates of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures were analysed. Change in World Health Organization (WHO) functional class and survival rates were evaluated by treatment strategy. A total of 51 (32%) patients were assessed as operable and 109 (68%) were deemed inoperable. Thirty-one (61% of operable patients) underwent PEA. Patients treated with PEA, BPA(+MT) and MT alone were 50.9 ± 14.7, 62.9 ± 15.1 and 68.9 ± 12.7 years old, respectively. At the follow-up, PEA patients had the highest WHO functional class improvement. Patients treated with BPA(+MT) had significantly better survival than PEA (p = 0.04) and MT patients (p = 0.04; 2-year survival of 92%, 79% and 79%, respectively).
Conclusions: The CTEPH team ensures that necessary diagnostic procedures are performed. A relatively low proportion of patients was assessed by the CTEPH team as operable and underwent surgery, which in survivors resulted in the best functional improvement. Although patients undergoing BPA(+MT) were older than patients treated with PEA, their survival was better than patients subjected to PEA or MT alone. The reviews of this paper are available via the supplemental material section.
Keywords: balloon pulmonary angioplasty; chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension; multidisciplinary team; pulmonary endarterectomy; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Lang IM, Madani M. Update on chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 2014; 130: 508–518. - PubMed
-
- Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiery J-L, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endor. Eur Heart J 2016; 37: 67–119. - PubMed
-
- Fedullo P, Kerr KM, Kim NH, et al. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2011; 183: 1605–1613. - PubMed
-
- Madani MM, Auger WR, Pretorius V, et al. Pulmonary endarterectomy: recent changes in a single institution’s experience of more than 2,700 patients. Ann Thorac Surg 2012; 94: 97–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

