A Practical Approach to Polycystic Liver Disease
- PMID: 31879559
- PMCID: PMC6924961
- DOI: 10.1002/cld.864
A Practical Approach to Polycystic Liver Disease
Abstract
http://aasldpubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/hub/journal/10.1002/(ISSN)2046-2484/video/14-5-reading-patel a video presentation of this article http://aasldpubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/hub/journal/10.1002/(ISSN)2046-2484/video/14-5-interview-patel the interview with the author.
© 2019 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
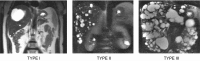
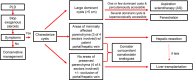
References
-
- Van Aerts RM, Van de Laarschot LF, Banales JM, et al. Clinical management of polycystic liver disease. J Hepatol 2018;68:827‐837. - PubMed
-
- Mikolajczyk AE, Te HS, Chapman AB. Gastrointestinal manifestations of autosomal‐dominant polycystic kidney disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;15:17‐24. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

