Effect of hydrocortisone on the 28-day mortality of patients with septic acute kidney injury
- PMID: 31880211
- PMCID: PMC6735306
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2019.1658605
Effect of hydrocortisone on the 28-day mortality of patients with septic acute kidney injury
Abstract
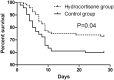
Objectives: To evaluate the efficacy of hydrocortisone in patients with septic acute kidney injury (SAKI).Methods: This retrospective cohort study consisted of all consecutive patients with SAKI who were admitted to the Taizhou First People's Hospital from March 2016 to February 2018. The patients who were treated with usual care including antibiotics, fluid resuscitation, and blood glucose control were regarded as the control group, and those received add-on hydrocortisone by the clinicians' discretion was considered in the intervention group. Hydrocortisone was administered as a 50 mg intravenous bolus every six hours for seven days. To adjust the potential baseline differences between the hydrocortisone and control groups, a 1:1 propensity score matching (PSM) was performed to identify a matched control subject for each patient in the hydrocortisone group.Results: In the propensity-matched cohort, the 28-day mortality was significantly lower for patients in the hydrocortisone group (p = .04). Both Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II and the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) scores were significantly lower at day 7 in the hydrocortisone group (both p < .01). Serum IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α concentrations significantly decreased for hydrocortisone group at day 7 (all p < .01). The levels of serum creatinine (SCr), Cystatin C (CysC), and procalcitonin (PCT) were significantly lower, while the levels of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and urine volume were significantly higher for hydrocortisone group at day 7 (all p < .01).Conclusions: Glucocorticoid supplementation may improve renal function and reduce the 28-day mortality of patients with SAKI.
Keywords: Hydrocortisone; acute kidney injury; mortality; sepsis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Efficacy of Hydrocortisone Combined With Norepinephrine in the Treatment of Severe Septic Shock and Its Effect on Immunoinflammatory Indexes.Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2025 Apr 25;86(4):1-13. doi: 10.12968/hmed.2024.0814. Epub 2025 Apr 22. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40265536
-
[Prognostic value of Charlson weighted index of comorbidities combined with sequential organ failure assessment score and procalcitonin in patients with sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Nov;31(11):1335-1339. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.11.005. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 31898562 Chinese.
-
Effect of stress doses of hydrocortisone on S-100B vs. interleukin-8 and polymorphonuclear elastase levels in human septic shock.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2005;43(3):259-68. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2005.044. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2005. PMID: 15843228 Clinical Trial.
-
The early diagnosis and pathogenic mechanisms of sepsis-related acute kidney injury.Open Life Sci. 2023 Aug 31;18(1):20220700. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0700. eCollection 2023. Open Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37671089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Response of Macrophages in Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 31;12(3):1101. doi: 10.3390/jcm12031101. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36769749 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Discrimination of Chronic Kidney Disease and Diabetic Nephropathy and Analysis of Their Related Influencing Factors.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020 Dec 30;13:5085-5096. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S275398. eCollection 2020. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020. PMID: 33408492 Free PMC article.
-
Association of glucocorticoids with outcomes in critically ill patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: a multicenter retrospective cohort study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20885. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05515-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594166 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Analysis of Blood Glucose Level with Inflammatory Response and Immune Indicators in Patients with Sepsis.Dis Markers. 2022 May 26;2022:8779061. doi: 10.1155/2022/8779061. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35664433 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of acute and chronic hydrocortisone treatment on pyroptosis.Heliyon. 2024 May 11;10(10):e31156. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31156. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38784563 Free PMC article.
-
Divergence between serum creatine and cystatin C in estimating glomerular filtration rate of critically ill COVID-19 patients.Ren Fail. 2021 Dec;43(1):1104-1114. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2021.1948428. Ren Fail. 2021. PMID: 34238117 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagshaw SM, Uchino S, Bellomo R, et al. . Septic acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: clinical characteristics and outcomes. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;2:431–439. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
