The Biological Impacts of Sitagliptin on the Pancreas of a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Drug Interactions with Metformin
- PMID: 31881657
- PMCID: PMC7167819
- DOI: 10.3390/biology9010006
The Biological Impacts of Sitagliptin on the Pancreas of a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Drug Interactions with Metformin
Erratum in
-
Correction: Shawky et al. The Biological Impacts of Sitagliptin on the Pancreas of a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Drug Interactions with Metformin. Biology 2020, 9, 6.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jul 16;13(7):527. doi: 10.3390/biology13070527. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056745 Free PMC article.
Abstract
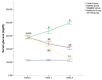
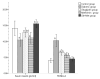
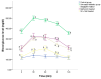
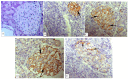
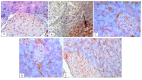
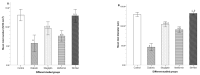
Sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor, is a beneficial class of antidiabetic drugs. However, a major debate about the risk of developing pancreatitis is still existing. The aim of the work was to study the histological and immunohistochemical effects of sitagliptin on both endocrine and exocrine pancreases in a rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus and to correlate these effects with the biochemical findings. Moreover, a possible synergistic effect of sitagliptin, in combination with metformin, was also evaluated. Fifty adult male rats were used and assigned into five equal groups. Group 1 served as control. Group 2 comprised of untreated diabetic rats. Group 3 diabetic rats received sitagliptin. Group 4 diabetic rats received metformin. Group 5 diabetic rats received both combined. Treatments were given for 4 weeks after the induction of diabetes. Blood samples were collected for biochemical assay before the sacrification of rats. Pancreases were removed, weighed, and were processed for histological and immunohistochemical examination. In the untreated diabetic group, the islets appeared shrunken with disturbed architecture and abnormal immunohistochemical reactions for insulin, caspase-3, and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). The biochemical findings were also disturbed. Morphometrically, there was a significant decrease in the islet size and islet number. Treatment with sitagliptin, metformin, and their combination showed an improvement, with the best response in the combined approach. No evidence of pancreatic injury was identified in the sitagliptin-treated groups. In conclusion, sitagliptin had a cytoprotective effect on beta-cell damage. Furthermore, the data didn't indicate any detrimental effects of sitagliptin on the exocrine pancreas.
Keywords: HFD/STZ diabetes; caspase-3; iNOS; immunohistochemistry; insulin; pancreas; rat; sitagliptin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
One year of sitagliptin treatment protects against islet amyloid-associated β-cell loss and does not induce pancreatitis or pancreatic neoplasia in mice.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Aug 15;305(4):E475-84. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00025.2013. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23736544 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial endocrine but adverse exocrine effects of sitagliptin in the human islet amyloid polypeptide transgenic rat model of type 2 diabetes: interactions with metformin.Diabetes. 2009 Jul;58(7):1604-15. doi: 10.2337/db09-0058. Epub 2009 Apr 29. Diabetes. 2009. PMID: 19403868 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the exocrine pancreas in the male Zucker diabetic fatty rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus following 3 months of treatment with sitagliptin.Endocrinology. 2014 Mar;155(3):783-92. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1781. Epub 2014 Jan 1. Endocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24424056
-
Sitagliptin prevents aggravation of endocrine and exocrine pancreatic damage in the Zucker Diabetic Fatty rat - focus on amelioration of metabolic profile and tissue cytoprotective properties.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2014 Mar 20;6(1):42. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-6-42. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2014. PMID: 24650557 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of DPP-4: a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.Curr Med Res Opin. 2007 Apr;23(4):919-31. doi: 10.1185/030079906x162746. Curr Med Res Opin. 2007. PMID: 17407649 Review.
Cited by
-
Melatonin downregulates the increased hepatic alpha-fetoprotein expression and restores pancreatic beta cells in a streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat model: a clinical, biochemical, immunohistochemical, and descriptive histopathological study.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Aug 16;10:1214533. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1214533. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37655263 Free PMC article.
-
Arabic gum ameliorates systemic modulation in Alloxan monohydrate-induced diabetic rats.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 27;13(1):5005. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31897-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36973339 Free PMC article.
-
Leiurus quinquestratus venom promotes β islets regeneration and restores glucose level in streptozotocin induced type 2 diabetes mellitus in rats.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 7;15(1):11841. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-94030-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40195395 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of metabolic pathways and serum biomarkers in diabetic cardiomyopathy using untargeted metabolomics.Sci Rep. 2025 May 28;15(1):18718. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98753-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40437131 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Effects of Metformin, Quercetin, and Fractionated Gamma Irradiation on MiR-107-Mediated Brain Injury in HFD/STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats.Dose Response. 2025 Aug 11;23(3):15593258251367627. doi: 10.1177/15593258251367627. eCollection 2025 Jul-Sep. Dose Response. 2025. PMID: 40801060 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mega C., Vala H., Rodrigues-Santos P., Oliveira J., Teixeira F., Fernandes R., Reis F., de Lemos E.T. Sitagliptin prevents aggravation of endocrine and exocrine pancreatic damage in the Zucker Diabetic Fatty rat—Focus on amelioration of metabolic profile and tissue cytoprotective properties. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014;6:42. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-6-42. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

