Reversibly pH-responsive gold nanoparticles and their applications for photothermal cancer therapy
- PMID: 31882911
- PMCID: PMC6934723
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-56754-8
Reversibly pH-responsive gold nanoparticles and their applications for photothermal cancer therapy
Abstract
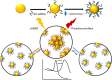
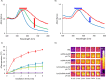
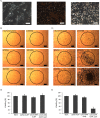
Microenvironment responsive nanomaterials are attractive for therapeutic applications with regional specificity. Here we report pH responsive gold nanoparticles which are designed to aggregate in acidic condition similar to cancer environment and returned to its original disassembled states in a physiological pH. The pH responsive behavior of the particles is derived by change of electrostatic interaction among the particles where attraction and repulsion play a major role in low and high pH of the environment, respectively. Since different electrostatic interaction behavior of the particles in varied pH is induced not by irreversible chemical change but by simple protonation differences, the pH responsive process of assembly and disassembly is totally reversible. The low pH specific aggregation of gold nanoparticles resulted in red shift of plasmonic absorption peak and showed higher photothermal efficacy in acidic pH than in normal physiological pH. The low pH specific photothermal effect with long wave laser irradiation was directly applied to cancer specific photothermal therapy and resulted higher therapeutic effect for melanoma cancer cells than non-pH responsive gold nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
pH-Induced aggregation of gold nanoparticles for photothermal cancer therapy.J Am Chem Soc. 2009 Sep 30;131(38):13639-45. doi: 10.1021/ja902062j. J Am Chem Soc. 2009. PMID: 19772360
-
Cancer Cell-Specific Enhanced Raman Imaging and Photothermal Therapeutic Effect Based on Reversibly pH-Responsive Gold Nanoparticles.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021 Dec 20;4(12):8377-8385. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.1c00946. Epub 2021 Nov 9. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021. PMID: 35005927
-
"Mixed-charge self-assembled monolayers" as a facile method to design pH-induced aggregation of large gold nanoparticles for near-infrared photothermal cancer therapy.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(21):18930-7. doi: 10.1021/am504813f. Epub 2014 Oct 20. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014. PMID: 25286378
-
Plasmonic photothermal therapy (PPTT) using gold nanoparticles.Lasers Med Sci. 2008 Jul;23(3):217-28. doi: 10.1007/s10103-007-0470-x. Epub 2007 Aug 3. Lasers Med Sci. 2008. PMID: 17674122 Review.
-
Gold nanostructures absorption capacities of various energy forms for thermal therapy applications.J Therm Biol. 2019 Jan;79:81-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2018.12.007. Epub 2018 Dec 10. J Therm Biol. 2019. PMID: 30612690 Review.
Cited by
-
Facile fabrication of hierarchically nanostructured gold electrode for bio-electrochemical applications.J Electroanal Chem (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 1;924:116865. doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2022.116865. Epub 2022 Oct 3. J Electroanal Chem (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36405880 Free PMC article.
-
Spectrophotometric Analysis and Optimization of 2D Gold Nanosheet Formation.J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2023 Feb 6;127(6):3067-3076. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.2c07582. eCollection 2023 Feb 16. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2023. PMID: 36824584 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-Functionalized Gold Nanospheres with Tunable Photothermal Efficiency for the Near-Infrared Photothermal Ablation of Biofilms.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Jan 31;16(4):4321-4332. doi: 10.1021/acsami.3c13288. Epub 2024 Jan 18. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38236953 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-Mineral Composite Particles with Logarithmic Dependence of Anticancer Cytotoxicity on Concentration of Montmorillonite Nanoplates with Adsorbed Cytochrome c.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 23;15(2):386. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020386. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839708 Free PMC article.
-
Conjugation of microbial-derived gold nanoparticles to different types of nucleic acids: evaluation of transfection efficiency.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 6;13(1):14669. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41567-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37674013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Piella J, Bastus NG, Puntes V. Size-Controlled Synthesis of Sub-10-nanometer Citrate-Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles and Related Optical Properties. Chem. Mater. 2016;28:1066–1075. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b04406. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

