MicroRNAs and their targeted genes associated with phase changes of stem explants during tissue culture of tea plant
- PMID: 31882926
- PMCID: PMC6934718
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-56686-3
MicroRNAs and their targeted genes associated with phase changes of stem explants during tissue culture of tea plant
Abstract
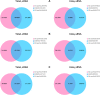
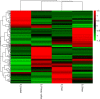
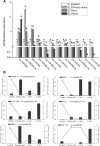
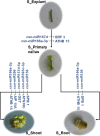
Elucidation of the molecular mechanism related to the dedifferentiation and redifferentiation during tissue culture will be useful for optimizing regeneration system of tea plant. In this study, an integrated sRNAome and transcriptome analyses were carried out during phase changes of the stem explant culture. Among 198 miRNAs and 8001 predicted target genes, 178 differentially expressed miRNAs and 4264 potential targets were screened out from explants, primary calli, as well as regenerated roots and shoots. According to KEGG analysis of the potential targets, pathway of "aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis", "proteasome" and "glutathione metabolism" was of great significance during the dedifferentiation, and pathway of "porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism", "mRNA surveillance pathway", "nucleotide excision repair" was indispensable for redifferentiation of the calli. Expression pattern of 12 miRNAs, including csn-micR390e, csn-miR156b-5p, csn-miR157d-5p, csn-miR156, csn-miR166a-3p, csn-miR166e, csn-miR167d, csn-miR393c-3p, csn-miR394, csn-miR396a-3p, csn-miR396 and csn-miR396e-3p, was validated by qRT-PCR among 57 differentially expressed phase-specific miRNAs. Validation also confirmed that regulatory module of csn-miR167d/ERF3, csn-miR156/SPB1, csn-miR166a-3p/ATHB15, csn-miR396/AIP15A, csn-miR157d-5p/GST and csn-miR393c-3p/ATG18b might play important roles in regulating the phase changes during tissue culture of stem explants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification of conserved and novel microRNAs in one bud and two tender leaves of tea plant (Camellia sinensis) by small RNA sequencing, microarray-based hybridization and genome survey scaffold sequences.BMC Plant Biol. 2017 Nov 21;17(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1169-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 29157210 Free PMC article.
-
Combined small RNA and degradome sequencing reveals complex microRNA regulation of catechin biosynthesis in tea (Camellia sinensis).PLoS One. 2017 Feb 22;12(2):e0171173. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171173. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28225779 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis of miRNAs and their targets reveals that miR319c/TCP2 regulates apical bud burst in tea plant (Camellia sinensis).Planta. 2019 Oct;250(4):1111-1129. doi: 10.1007/s00425-019-03207-1. Epub 2019 Jun 6. Planta. 2019. PMID: 31172343
-
Absolute quantification of microRNAs in green tea (Camellia sinensis) by stem-loop quantitative real-time PCR.J Sci Food Agric. 2017 Jul;97(9):2975-2981. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.8137. Epub 2016 Dec 21. J Sci Food Agric. 2017. PMID: 27861949
-
Screening of differentially expressed microRNAs and target genes in two potato varieties under nitrogen stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Oct 8;22(1):478. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03866-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 36207676 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome analysis revealed enrichment pathways and regulation of gene expression associated with somatic embryogenesis in Camellia sinensis.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 24;13(1):15946. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43355-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37743377 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory roles of noncoding RNAs in callus induction and plant cell dedifferentiation.Plant Cell Rep. 2023 Apr;42(4):689-705. doi: 10.1007/s00299-023-02992-0. Epub 2023 Feb 8. Plant Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 36753041 Review.
-
miRNA expression profiling and zeatin dynamic changes in a new model system of in vivo indirect regeneration of tomato.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 17;15(12):e0237690. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237690. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33332392 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory non-coding RNAs: Emerging roles during plant cell reprogramming and in vitro regeneration.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Nov 10;13:1049631. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1049631. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36438127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiRNA fine tuning for crop improvement: using advance computational models and biotechnological tools.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jun;49(6):5437-5450. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07231-5. Epub 2022 Feb 19. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35182321 Review.
References
-
- Jung JH, Seo PJ, Park CM. MicroRNA biogenesis and function in higher plants. Plant Biotechnol Rep. 2009;3:111–126. doi: 10.1007/s11816-009-0085-8. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

