Loss-of-Function Variants in PPP1R12A: From Isolated Sex Reversal to Holoprosencephaly Spectrum and Urogenital Malformations
- PMID: 31883643
- PMCID: PMC7042489
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.12.004
Loss-of-Function Variants in PPP1R12A: From Isolated Sex Reversal to Holoprosencephaly Spectrum and Urogenital Malformations
Abstract
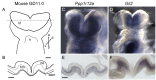
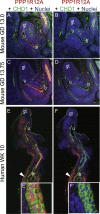
In two independent ongoing next-generation sequencing projects for individuals with holoprosencephaly and individuals with disorders of sex development, and through international research collaboration, we identified twelve individuals with de novo loss-of-function (LoF) variants in protein phosphatase 1, regulatory subunit 12a (PPP1R12A), an important developmental gene involved in cell migration, adhesion, and morphogenesis. This gene has not been previously reported in association with human disease, and it has intolerance to LoF as illustrated by a very low observed-to-expected ratio of LoF variants in gnomAD. Of the twelve individuals, midline brain malformations were found in five, urogenital anomalies in nine, and a combination of both phenotypes in two. Other congenital anomalies identified included omphalocele, jejunal, and ileal atresia with aberrant mesenteric blood supply, and syndactyly. Six individuals had stop gain variants, five had a deletion or duplication resulting in a frameshift, and one had a canonical splice acceptor site loss. Murine and human in situ hybridization and immunostaining revealed PPP1R12A expression in the prosencephalic neural folds and protein localization in the lower urinary tract at critical periods for forebrain division and urogenital development. Based on these clinical and molecular findings, we propose the association of PPP1R12A pathogenic variants with a congenital malformations syndrome affecting the embryogenesis of the brain and genitourinary systems and including disorders of sex development.
Keywords: MYPT1; PPP1R12A; disorders of sex development; embryogenesis; encephalocele; facial dysmorphism; forebrain; holoprosencephaly; hypospadias; omphalocele.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
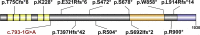
References
-
- Grassie M.E., Moffat L.D., Walsh M.P., MacDonald J.A. The myosin phosphatase targeting protein (MYPT) family: a regulated mechanism for achieving substrate specificity of the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase type 1δ. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011;510:147–159. - PubMed
-
- Kiss A., Erdődi F., Lontay B. Myosin phosphatase: Unexpected functions of a long-known enzyme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019;1866:2–15. - PubMed
-
- Ito M., Nakano T., Erdodi F., Hartshorne D.J. Myosin phosphatase: structure, regulation and function. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2004;259:197–209. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu H., Ito M., Miyahara M., Ichikawa K., Okubo S., Konishi T., Naka M., Tanaka T., Hirano K., Hartshorne D.J. Characterization of the myosin-binding subunit of smooth muscle myosin phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:30407–30411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

