Emerging organoid models: leaping forward in cancer research
- PMID: 31884964
- PMCID: PMC6936115
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-019-0832-4
Emerging organoid models: leaping forward in cancer research
Abstract
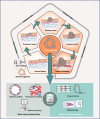
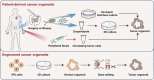
Cancer heterogeneity is regarded as the main reason for the failure of conventional cancer therapy. The ability to reconstruct intra- and interpatient heterogeneity in cancer models is crucial for understanding cancer biology as well as for developing personalized anti-cancer therapy. Cancer organoids represent an emerging approach for creating patient-derived in vitro cancer models that closely recapitulate the pathophysiological features of natural tumorigenesis and metastasis. Meanwhile, cancer organoids have recently been utilized in the discovery of personalized anti-cancer therapy and prognostic biomarkers. Further, the synergistic combination of cancer organoids with organ-on-a-chip and 3D bioprinting presents a new avenue in the development of more sophisticated and optimized model systems to recapitulate complex cancer-stroma or multiorgan metastasis. Here, we summarize the recent advances in cancer organoids from a perspective of the in vitro emulation of natural cancer evolution and the applications in personalized cancer theranostics. We also discuss the challenges and trends in reconstructing more comprehensive cancer models for basic and clinical cancer research.
Keywords: 3D Bioprinting; Cancer heterogeneity; Cancer organoids; In vitro model system; Organ-on-a-chip; Patient-derived tumor organoids; Personalized anti-cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Society AC. Global Cancer Facts & Figures 3rd Edition. Am Cancer Soc. 2015;800:1–64.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

