Early detection of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portsystemic shunt using multiparametric magnetic resonance with spectroscopy
- PMID: 31886319
- PMCID: PMC6909044
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejro.2019.09.002
Early detection of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portsystemic shunt using multiparametric magnetic resonance with spectroscopy
Abstract
Background: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a complication of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS).
Aims: Extend the knowledge about the early detection of multiple brain metabolic abnormalities following TIPS; these abnormalities can be detected and managed prior to the clinical manifestation of HE with use of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance with Spectroscopy.
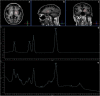
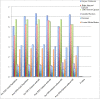
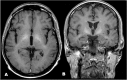
Methods: 12 cirrhotic Patients underwent TIPS; each Patient underwent a 3 T MRI evaluation before and after TIPS. The spectroscopic images were processed measuring the values of the metabolites N-acetylaspartate (NAA) - Glutamine / Glutamate (Glx) - Colina (Cho) - Myinositol (mI) at the level of the nuclei of the base.
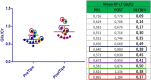
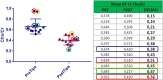
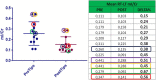
Results: Spectroscopic examination performed before the TIPS procedure showed low values of Cho and Mi, instead following the procedure: an increase in the Glx value, a mean reduction in the values of Cho and mI, a statistically significant reduction in the Cho / Creatine ratio, in the mI / Creatine ratio and an increase of the Glx / Creatine ratio.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrated the efficacy of spectroscopy in Patient subjected to TIPS. MR 3 T with spectroscopy can become a valid tool for monitor the dynamics of changes in brain metabolism after TIPS and to provide an early diagnosis of HE allowing an early treatment.
Keywords: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE); Multiparametric magnetic resonance; Spectroscopy; Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS).
© 2019 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Proton MR spectroscopic measurement of neurometabolites in hepatic encephalopathy during oral lactulose therapy.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998 Oct;19(9):1681-6. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998. PMID: 9802491 Free PMC article.
-
Differential impact of hyponatremia and hepatic encephalopathy on health-related quality of life and brain metabolite abnormalities in cirrhosis.J Hepatol. 2013 Sep;59(3):467-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.04.023. Epub 2013 May 7. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23665182 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric dimethylarginine is strongly associated with cognitive dysfunction and brain MR spectroscopic abnormalities in cirrhosis.J Hepatol. 2013 Jan;58(1):38-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.08.005. Epub 2012 Aug 11. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 22889958 Free PMC article.
-
The brain following transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: the perspective from neuroimaging.Metab Brain Dis. 2015 Dec;30(6):1331-41. doi: 10.1007/s11011-015-9735-4. Epub 2015 Sep 24. Metab Brain Dis. 2015. PMID: 26404041 Review.
-
Current diagnosis and management of post-transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt refractory hepatic encephalopathy.Liver Int. 2015 Dec;35(12):2487-94. doi: 10.1111/liv.12956. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Liver Int. 2015. PMID: 26332169 Review.
References
-
- Javier Vaquero M.D., Chuhan Chung M.D., Michael E., Cahill B.A., Blei Andres T. Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy in acute liver failure. MD Semin Liver Dis. 2003;23(3) - PubMed
-
- Bai M., Qi X., Yang Z., Yin Z., Nie Y., Yuan S., Wu K., Han G., Fan D. Predictors of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in cirrhotic patients: a systematic review. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011;26(6):943–951. - PubMed
-
- Colombato L. The role of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) in the management of portal hypertension. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007;41(3):S344–51. no. December. - PubMed
-
- Hassoun Z., Deschênes M., Lafortune M., Dufresne M.P., Perreault P., Lepanto L., Gianfelice D., Bui B., Pomier-Layrargues G. Relationship between pre-TIPS liver perfusion by the portal vein and the incidence of post-TIPS chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001;96(4):1205–1209. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

