Inhibition deficits are modulated by age and CGG repeat length in carriers of the FMR1 premutation allele who are mothers of children with fragile X syndrome
- PMID: 31887710
- PMCID: PMC6954879
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bandc.2019.105511
Inhibition deficits are modulated by age and CGG repeat length in carriers of the FMR1 premutation allele who are mothers of children with fragile X syndrome
Abstract
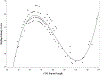
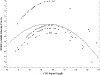
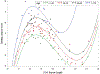
Individuals who carry a premutation (PM) allele on the FMR1 gene may experience executive limitations associated with their genetic status, including inhibition deficits. However, poor understanding of individualized risk factors has limited clinical management of this group, particularly in mothers who carry the PM allele who have children with fragile X syndrome (FXS). The present study examined CGG repeat length and age as factors that may account for variable expressivity of inhibition deficits. Participants were 134 carriers of the PM allele who were mothers of children with FXS. Inhibition skills were measured using both self-report and direct behavioral assessments. Increased vulnerability for inhibition deficits was observed at mid-range CGG lengths of approximately 80-100 repeats, with some evidence of a second zone of vulnerability occurring at approximately 130-140 CGG repeats. Risk associated with the genotype also became more pronounced with older age. This study identifies personalized risk factors that may be used to tailor the clinical management of executive deficits in carriers of the PM allele. Inhibition deficits may contribute to poor outcomes in carriers of the PM allele and their families, particularly in midlife and early old age, and clinical monitoring may be warranted.
Keywords: FMR1 premutation; age effects; executive dysfunction; fragile X premutation carrier; mid-range CGG.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploring inhibitory deficits in female premutation carriers of fragile X syndrome: through eye movements.Brain Cogn. 2014 Mar;85:201-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2013.12.006. Epub 2014 Jan 11. Brain Cogn. 2014. PMID: 24424424
-
Immune dysregulation as a cause of autoinflammation in fragile X premutation carriers: link between FMRI CGG repeat number and decreased cytokine responses.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 9;9(4):e94475. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094475. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24718368 Free PMC article.
-
Static and dynamic postural control deficits in aging fragile X mental retardation 1 (FMR1) gene premutation carriers.J Neurodev Disord. 2019 Jan 21;11(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s11689-018-9261-x. J Neurodev Disord. 2019. PMID: 30665341 Free PMC article.
-
[FMR1 PREMUTATION CARRIERS - ARE THEY REALLY ASYMPTOMATIC?].Harefuah. 2018 Apr;157(4):241-244. Harefuah. 2018. PMID: 29688643 Review. Hebrew.
-
Does theFMR1 gene affect IVF success?Reprod Biomed Online. 2019 Apr;38(4):560-569. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2018.11.009. Epub 2018 Dec 10. Reprod Biomed Online. 2019. PMID: 30711457 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of college degree attainment on neurodegenerative symptoms in genetically at-risk women.SSM Popul Health. 2022 Oct 5;19:101262. doi: 10.1016/j.ssmph.2022.101262. eCollection 2022 Sep. SSM Popul Health. 2022. PMID: 36238818 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical vocal quality in women with the FMR1 premutation: an indicator of impaired sensorimotor control.Exp Brain Res. 2023 Aug;241(8):1975-1987. doi: 10.1007/s00221-023-06653-2. Epub 2023 Jun 22. Exp Brain Res. 2023. PMID: 37347418 Free PMC article.
-
Family history of FXTAS is associated with age-related cognitive-linguistic decline among mothers with the FMR1 premutation.J Neurodev Disord. 2022 Jan 14;14(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s11689-022-09415-3. J Neurodev Disord. 2022. PMID: 35026985 Free PMC article.
-
Activation Ratio Correlates with IQ in Female Carriers of the FMR1 Premutation.Cells. 2023 Jun 24;12(13):1711. doi: 10.3390/cells12131711. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37443745 Free PMC article.
-
Verbal inhibition declines among older women with high FMR1 premutation expansions: A prospective study.Brain Cogn. 2022 Jun;159:105851. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2022.105851. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Brain Cogn. 2022. PMID: 35279590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen E, Sullivan A, Marcus M, Small C, Dominguez C, Epstein M, et al. (2007). Examination of reproductive aging milestones among women who carry the FMR1 premutation. Human reproduction, 22(8), 2142–2152. - PubMed
-
- Andrés P, & Van der Linden M (2000). Age-related differences in supervisory attentional system functions. The Journals of Gerontology: Series B, 55(6), P373–P380. - PubMed
-
- Battistella G, Niederhauser J, Fornari E, Hippolyte L, Gronchi Perrin A, Lesca G, et al. (2013). Brain structure in asymptomatic FMR1 premutation carriers at risk for fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome. Neurobiology of Aging, 34(6), 1700–1707. - PubMed
-
- Bielak AA, Mansueti L, Strauss E, & Dixon RA (2006). Performance on the Hayling and Brixton tests in older adults: Norms and correlates. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 21(2), 141–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

