The Protective Role of 28-Homobrassinolide and Glomus versiforme in Cucumber to Withstand Saline Stress
- PMID: 31888068
- PMCID: PMC7020224
- DOI: 10.3390/plants9010042
The Protective Role of 28-Homobrassinolide and Glomus versiforme in Cucumber to Withstand Saline Stress
Abstract
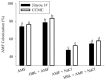
The strategic role of phytohormones and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) to overcome various stress conditions is gaining popularity in sustainable agricultural practices. This current study aims to investigate and identify the protective roles of 28-homobrassinolide (HBL) and Glomus versiforme on two cucumber cultivars (salt sensitive Jinyou 1# and tolerant Chanchun mici (CCMC)) grown under saline conditions (100 mM NaCl). HBL and AMF were applied as individual and combined treatments on two cucumber cultivars and their effects were observed on the morphological growth and physiology under control and saline conditions. Findings revealed that the treated plants showed better performance under saline conditions through improved photosynthesis, leaf relative water content, and decreased electrolyte leakage in tolerant cultivar (CCMC) and to a lesser extent in sensitive (Jinyou 1#) cultivar. Comparable differences were noticed in the antioxidant enzymes activity such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase after every 10 days in both cultivars. Treating the plants with HBL and AMF also improved the mineral uptake regulation and lowered sodium concentration in roots compared to that in the non-treated plants. Current findings suggest that the protective role of HBL and AMF involves the regulation of antioxidants and lowers the risk of ion toxicity in the cucumber and hence enhance tolerance to salinity. These results are promising, but further studies are needed to verify the crop tolerance to stress and help in sustainable agricultural production, particularly vegetables that are prone to salinity.
Keywords: 28-homobrassinolide; NaCl; antioxidant enzymes; arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The combination of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation (Glomus versiforme) and 28-homobrassinolide spraying intervals improves growth by enhancing photosynthesis, nutrient absorption, and antioxidant system in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) under salinity.Ecol Evol. 2018 May 10;8(11):5724-5740. doi: 10.1002/ece3.4112. eCollection 2018 Jun. Ecol Evol. 2018. PMID: 29938088 Free PMC article.
-
Native arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi isolated from a saline habitat improved maize antioxidant systems and plant tolerance to salinity.Plant Sci. 2013 Mar;201-202:42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2012.11.009. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 23352401
-
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Rhizophagus irregularis alleviates drought stress in soybean with overexpressing the GmSPL9d gene by promoting photosynthetic apparatus and regulating the antioxidant system.Microbiol Res. 2023 Aug;273:127398. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2023.127398. Epub 2023 May 3. Microbiol Res. 2023. PMID: 37167733
-
Role of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi in Regulating Growth, Enhancing Productivity, and Potentially Influencing Ecosystems under Abiotic and Biotic Stresses.Plants (Basel). 2023 Aug 29;12(17):3102. doi: 10.3390/plants12173102. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37687353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current developments in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi research and its role in salinity stress alleviation: a biotechnological perspective.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2015;35(4):461-74. doi: 10.3109/07388551.2014.899964. Epub 2014 Apr 7. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 24708070 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of water deficit on the development and senescence of tomato roots grown under various soil textures of Shaanxi, China.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 May 28;21(1):241. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03018-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 34049491 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell transcriptome sequencing reveals the sphingolipid metabolism pathway plays an important role in leaf senescence in tobacco.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Aug 6;25(1):1026. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-07051-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40764913 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms Regulating the Dynamics of Photosynthesis Under Abiotic Stresses.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Jan 28;11:615942. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.615942. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33584756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promotion of Ca2+ Accumulation in Roots by Exogenous Brassinosteroids as a Key Mechanism for Their Enhancement of Plant Salt Tolerance: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 9;24(22):16123. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216123. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003311 Free PMC article.
-
Crucial Roles of Brassinosteroids in Cell Wall Composition and Structure Across Species: New Insights and Biotechnological Applications.Plant Cell Environ. 2025 Mar;48(3):1751-1767. doi: 10.1111/pce.15258. Epub 2024 Nov 3. Plant Cell Environ. 2025. PMID: 39491539 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hashem A., Abd-Allah E.F., Alqarawi A.A., Al-Huqail A.A., Wirth S., Egamberdieva D. The interaction between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and endophytic bacteria enhances plant growth of Acacia gerrardii under salt stress. Front. Microbiol. 2016;7:1–15. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01089. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Flowers T.J., Yeo A. Breeding for salinity resistance in crop plants: Where next? Funct. Plant Biol. 1995;22:875–884. doi: 10.1071/PP9950875. - DOI
-
- Hayat S., Hasan S.A., Yusuf M., Hayat Q., Ahmad A. Effect of 28-homobrassinolide on photosynthesis, fluorescence and antioxidant system in the presence or absence of salinity and temperature in Vigna radiata. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2010;69:105–112. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2010.03.004. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

